133 KiB
| title | author | top | cover | toc | mathjax | summary | tags | categories | reprintPolicy | abbrlink | date | coverImg | img | password |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SpringBoot | TianZD | true | true | true | false | SpringBoot框架学习笔记,粗略学了一下,没有参考价值 | [SpringBoot 学习笔记] | [java] | cc_by | 6f2612a2 | 2022-04-29 11:07:58 | <nil> | <nil> | <nil> |
[toc]
SpringBoot
1、概述
1.1、学习总结
- JavaSE:oop
- mysql:持久化
- html+css+js+jquery+框架:视图
- javaWeb:独立开发MVC三层架构的网站
- ssm:框架:简化了开发的流程,配置繁琐
war包:tomcat运行
- spring简化:SpringBoot,jar包,内嵌tomcat,微服务架构
- springcloud:管理微服务
1.2、spring
Spring理念、目的
spring是为了解决企业级应用开发的复杂性创建的,简化开发
Spring如何简化开发
- 基于pojo的轻量级和最小入侵编程
- 通过IOC,依赖注入(DI)和面向接口实现松耦合
- 基于切面(AOP)和惯例进行声明式编程
- 通过切面和模板(template)减少样式代码
区别
程序=数据结构+算法:程序员
程序=面向对象+框架:码农
1.3、微服务
什么是微服务
微服务是一种架构风格,要求在开发一个应用的时候,应用必须构建成一系列小服务的组合,可以通过http的方式通信
单体运行架构
all in one,所用的应用服务都封装在一个应用中
微服务架构
打破all in one的架构方式,把每个功能元素苏里出来,把苏里出来的功能元素动态组合,需要的功能元素才去拿来组合,需要多一时可以整合多个功能元素,所以微服务架构是对功能元素进行复制,没有对整个应用进行复制
- 节省了调用资源
- 每个功能元素的服务都是一个可替换的,可独立升级的软件代码
1.4、SpringBoot
概述
Spring Boot 是由 Pivotal 团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新 Spring 应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。用我的话来理解,就是 Spring Boot 其实不是什么新的框架,它默认配置了很多框架的使用方式,就像 Maven 整合了所有的 Jar 包,Spring Boot 整合了所有的框架。
优势
其实就是简单、快速、方便!平时如果我们需要搭建一个 Spring Web 项目的时候需要怎么做呢?
- 1)配置 web.xml,加载 Spring 和 Spring mvc
- 2)配置数据库连接、配置 Spring 事务
- 3)配置加载配置文件的读取,开启注解
- 4)配置日志文件
- …
- 配置完成之后部署 Tomcat 调试
- …
现在非常流行微服务,如果我这个项目仅仅只是需要发送一个邮件,如果我的项目仅仅是生产一个积分;我都需要这样折腾一遍!
但是如果使用 Spring Boot 呢? 很简单,我仅仅只需要非常少的几个配置就可以迅速方便的搭建起来一套 Web 项目或者是构建一个微服务!
1.5、Spring Boot、Spring MVC 和 Spring
分别描述各自的特征:
-
Spring 框架就像一个家族,有众多衍生产品例如 boot、security、jpa等等;但他们的基础都是Spring 的ioc和 aop,ioc 提供了依赖注入的容器, aop解决了面向切面编程,然后在此两者的基础上实现了其他延伸产品的高级功能。
-
Spring MVC提供了一种轻度耦合的方式来开发web应用;它是Spring的一个模块,是一个web框架;通过DispatcherServlet, ModelAndView 和 View Resolver,开发web应用变得很容易;解决的问题领域是网站应用程序或者服务开发——URL路由、Session、模板引擎、静态Web资源等等。
-
Spring Boot实现了auto-configuration自动配置(另外三大神器actuator监控,cli命令行接口,starter依赖),降低了项目搭建的复杂度。它主要是为了解决使用Spring框架需要进行大量的配置太麻烦的问题,所以它并不是用来替代Spring的解决方案,而是和Spring框架紧密结合用于提升Spring开发者体验的工具;同时它集成了大量常用的第三方库配置(例如Jackson, JDBC, Mongo, Redis, Mail等等),Spring Boot应用中这些第三方库几乎可以零配置的开箱即用(out-of-the-box)。
所以,用最简练的语言概括就是:
-
Spring 是一个“引擎”;
-
Spring MVC 是基于Spring的一个 MVC 框架;
-
Spring Boot 是基于Spring4的条件注册的一套快速开发整合包。
2、SpringBoot程序
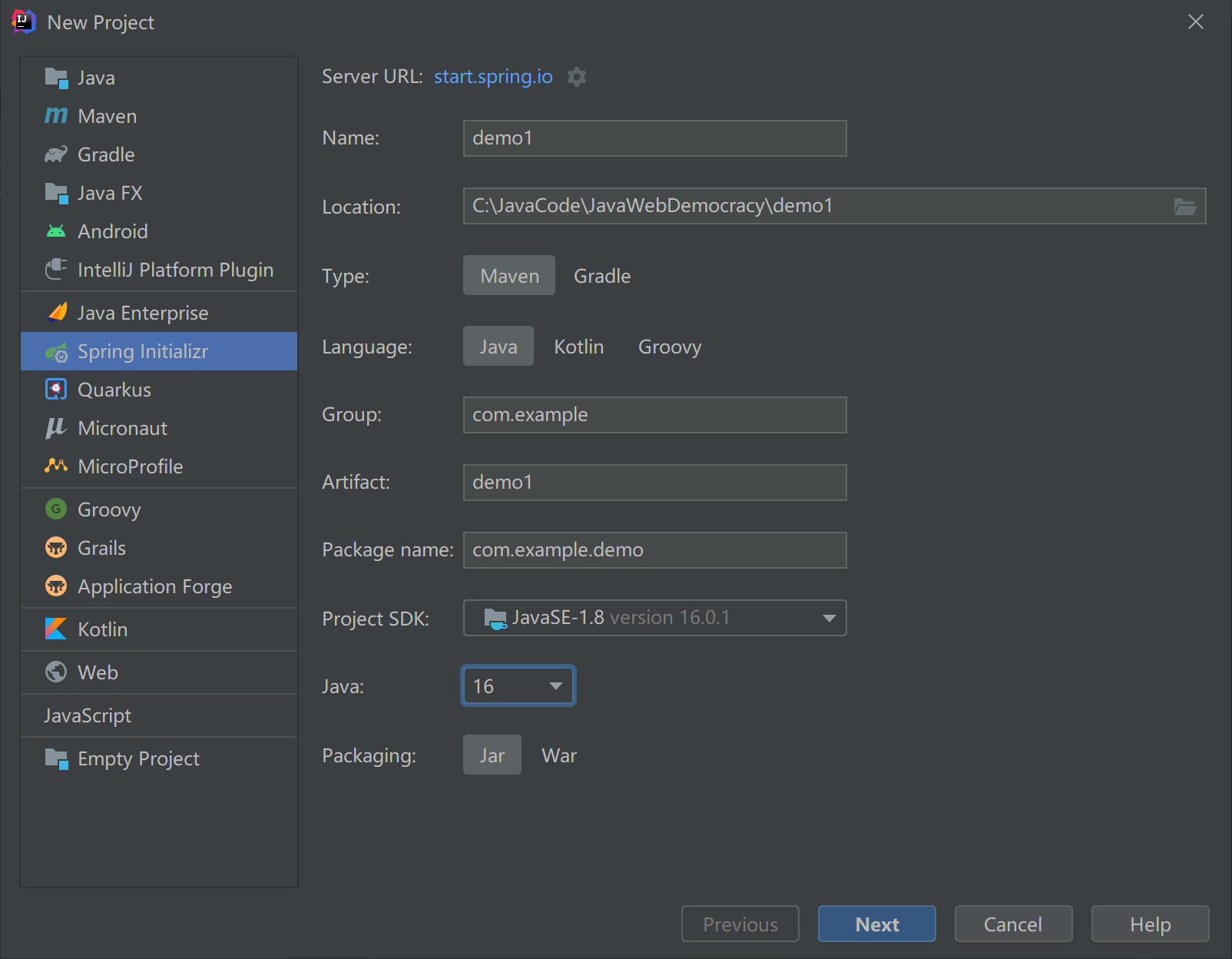
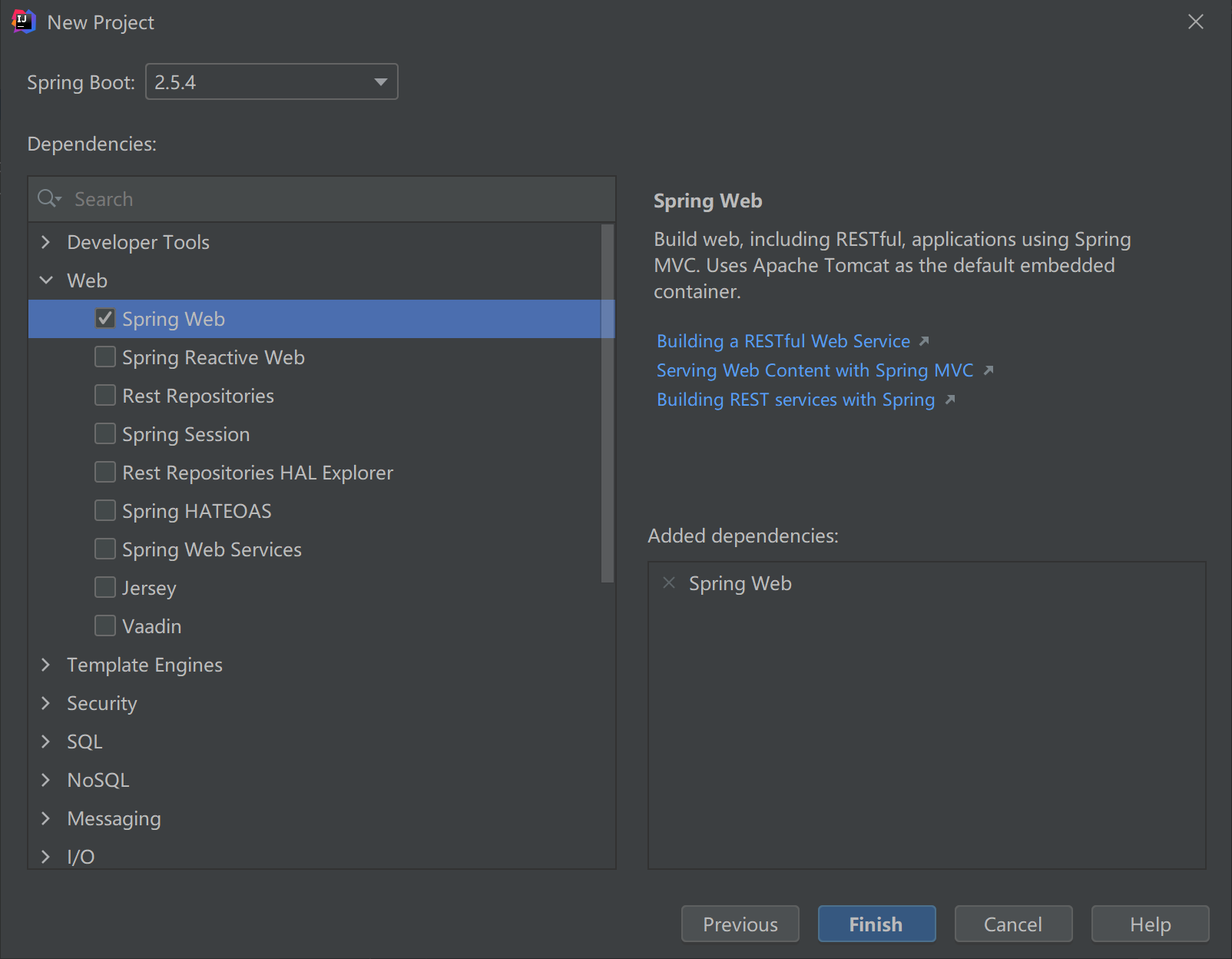
2.1、初始化
创建:
- IDEA新建项目,选择SpringInitializr
- 勾选SpringWeb
- 新建之后,删除多余文件
分析
默认自动生成一下文件
- springboot启动文件,启动器
package com.tian.springboot01helloworld;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot01HelloworldApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot01HelloworldApplication.class, args);
}
}
- application.properties,默认为空
- pop.xml 依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<!-- This module was also published with a richer model, Gradle metadata, -->
<!-- which should be used instead. Do not delete the following line which -->
<!-- is to indicate to Gradle or any Gradle module metadata file consumer -->
<!-- that they should prefer consuming it instead. -->
<!-- do_not_remove: published-with-gradle-metadata -->
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
<name>spring-boot-starter-web</name>
<description>Starter for building web, including RESTful, applications using Spring MVC. Uses Tomcat as the default embedded container</description>
<url>https://spring.io/projects/spring-boot</url>
<organization>
<name>Pivotal Software, Inc.</name>
<url>https://spring.io</url>
</organization>
<licenses>
<license>
<name>Apache License, Version 2.0</name>
<url>https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0</url>
</license>
</licenses>
<developers>
<developer>
<name>Pivotal</name>
<email>info@pivotal.io</email>
<organization>Pivotal Software, Inc.</organization>
<organizationUrl>https://www.spring.io</organizationUrl>
</developer>
</developers>
<scm>
<connection>scm:git:git://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot.git</connection>
<developerConnection>scm:git:ssh://git@github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot.git</developerConnection>
<url>https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot</url>
</scm>
<issueManagement>
<system>GitHub</system>
<url>https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/issues</url>
</issueManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-json</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.3.9</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.9</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
- 测试文件
package com.tian.springboot01helloworld;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot01HelloworldApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
}
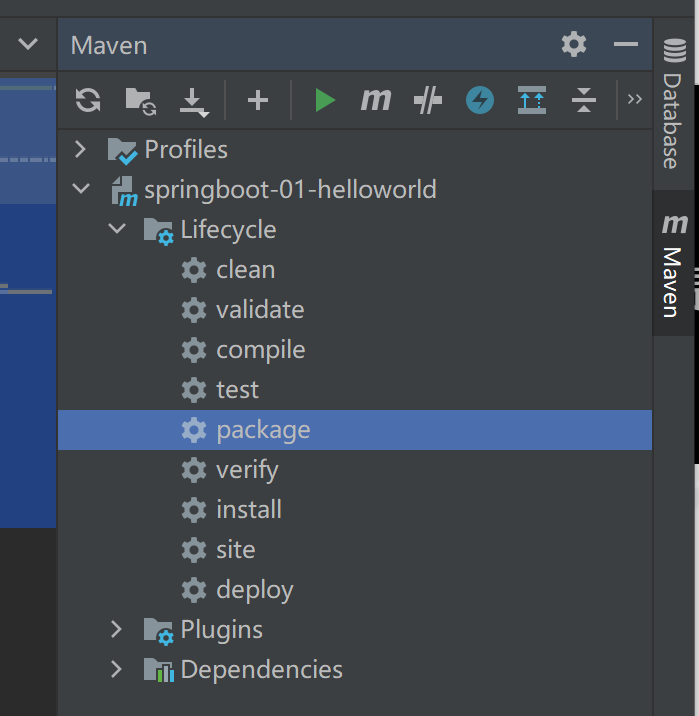
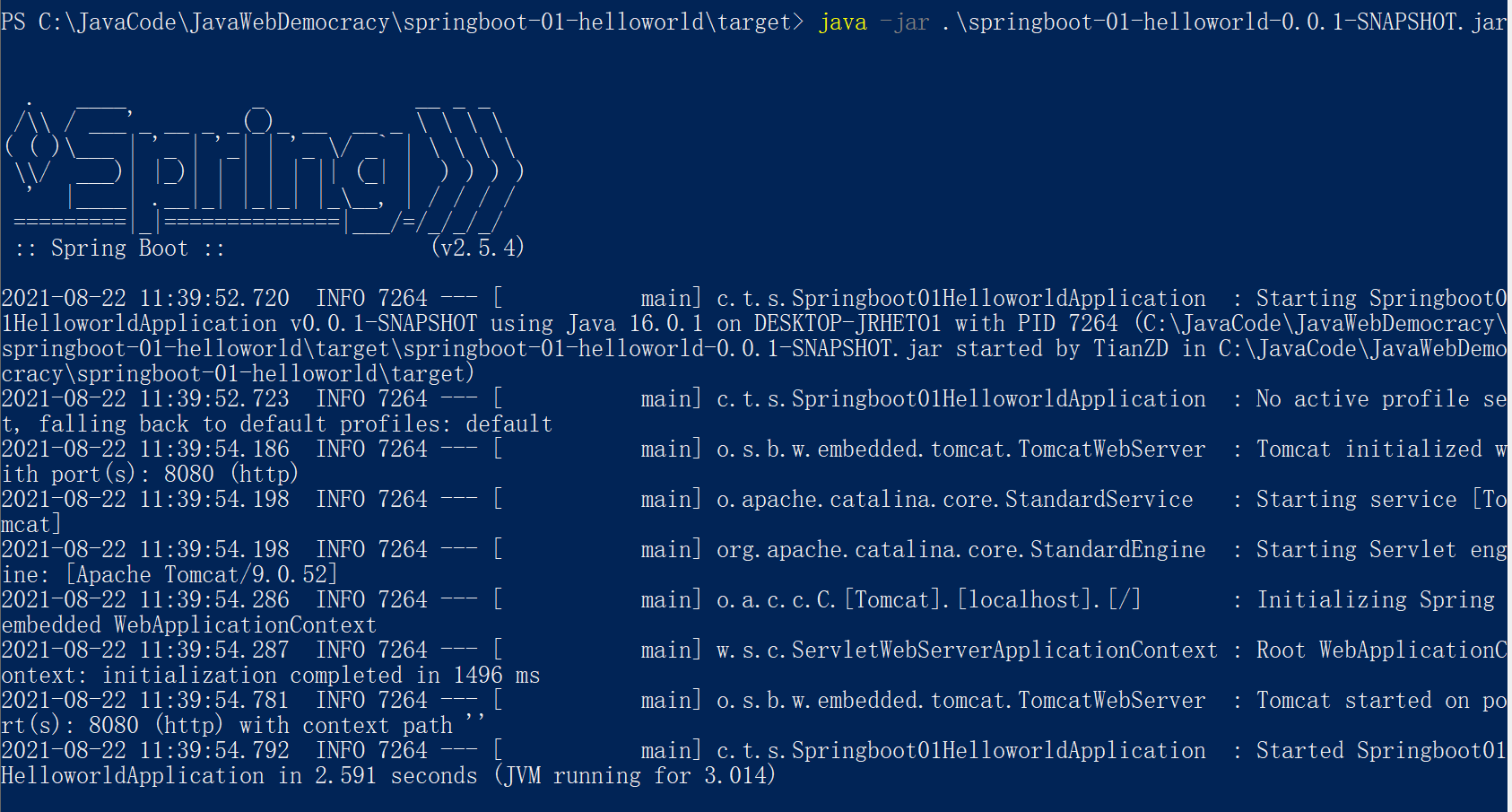
打jar包
- 在右侧maven中,双击package,自动打jar包
- 在target目录下,生成一个jar包
新建目录结构
在Springboot启动程序的同级目录下新建controller、dao、pojo、service
新建简单接口
package com.tian.springboot01helloworld.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
// 调用业务,接收前端参数
return "hello,world!";
}
}
@RestController 的意思就是 Controller 里面的方法都以 json 格式输出,不用再写什么 jackjson 配置的了!
浏览器访问
1.2、配置
更改项目端口号
application.properties
# 更改端口号
server.port=8081
更改banner
-
百度搜索springboot banner在线生成,并复制
-
在resources下创建
banner.txt,并粘贴进去
开发环境的热启动
热启动在正常开发项目中已经很常见了吧,虽然平时开发web项目过程中,改动项目启重启总是报错;但springBoot对调试支持很好,修改之后可以实时生效,需要添加以下的配置:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<fork>true</fork>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
该模块在完整的打包环境下运行的时候会被禁用。如果你使用 java -jar启动应用或者用一个特定的 classloader 启动,它会认为这是一个“生产环境”。
3、原理
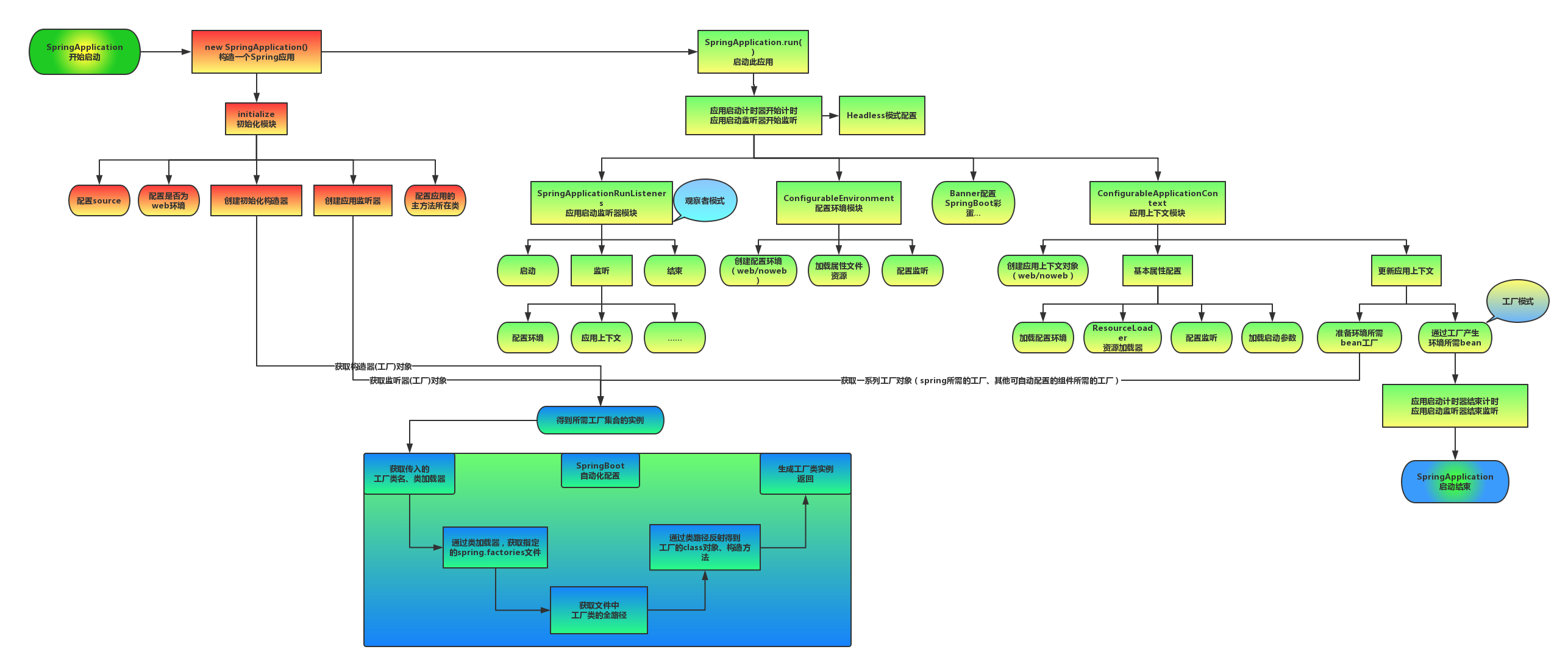
3.1、启动执行流程
上图为SpringBoot启动结构图,我们发现启动流程主要分为三个部分:
- 第一部分进行SpringApplication的初始化模块,配置一些基本的环境变量、资源、构造器、监听器;
- 第二部分实现了应用具体的启动方案,包括启动流程的监听模块、加载配置环境模块、及核心的创建上下文环境模块;
- 第三部分是自动化配置模块,该模块作为springboot自动配置核心,在后面的分析中会详细讨论。在下面的启动程序中我们会串联起结构中的主要功能。
3.2、入口
springboot有自己独立的启动类(独立程序)
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot01HelloworldApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot01HelloworldApplication.class, args);
}
}
主要包括:
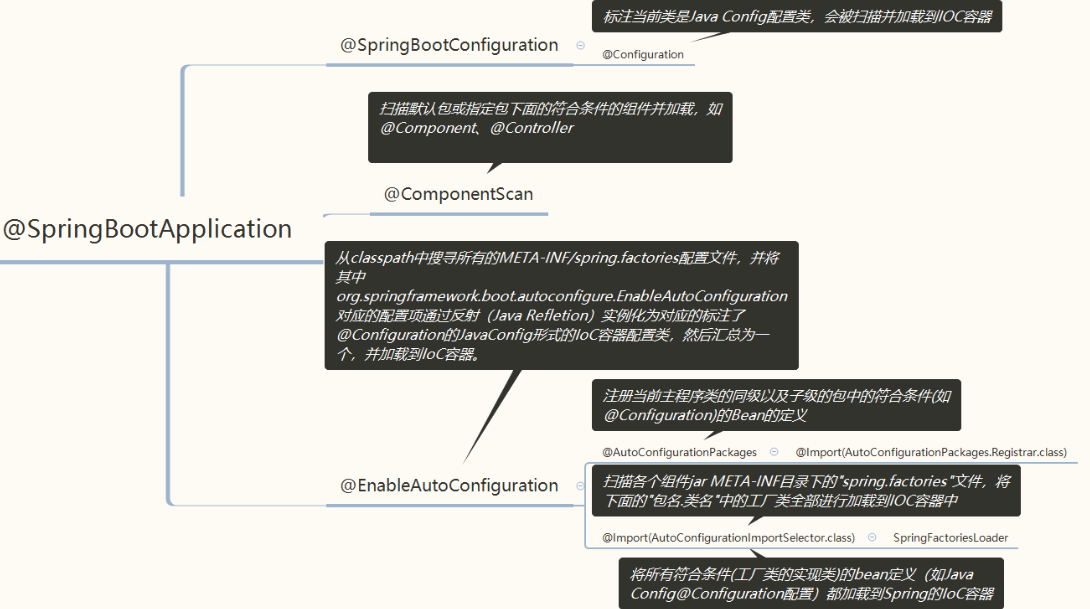
- Annotation定义(@SpringBootApplication),是Spring Boot的核心注解,它其实是一个组合注解
- 类定义(SpringApplication.run):启动整个spring-boot程序,该方法所在类需要使用
3.3、自动配置
3.3.1、@SpringBootApplication
@Target``(ElementType.TYPE) ``// 注解的适用范围,其中TYPE用于描述类、接口(包括包注解类型)或enum声明
@Retention``(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) ``// 注解的生命周期,保留到class文件中(三个生命周期)
@Documented` `// 表明这个注解应该被javadoc记录
@Inherited` `// 子类可以继承该注解
@SpringBootConfiguration` `// 继承了Configuration,表示当前是注解类
@EnableAutoConfiguration` `// 开启springboot的注解功能,springboot的四大神器之一,其借助@import的帮助
@ComponentScan``(excludeFilters = { ``// 扫描路径设置
@Filter``(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.``class``),
@Filter``(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.``class``) })
public` `@interface` `SpringBootApplication {
...
}
在其中比较重要的有三个注解,分别是:
- @SpringBootConfiguration // 继承了Configuration,表示当前是注解类
- @EnableAutoConfiguration // 开启自动配置
- @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { // 扫描路径设置(具体使用待确认)扫描主类所在的同级包以及下级包里的Bean
接下来对三个注解一一详解,增加对springbootApplication的理解:
@SpringBootConfiguration
在springboot中我们大多用配置类来解决配置问题
@SpringBootConfiguration继承了Configuration,表示当前是注解类
@Configuration实际上就是一个@Component,表示一个受Spring管理的组件
@ComponentScan
-
ComponentScan的功能其实就是自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件(比如@Component和@Repository等)或者bean定义,将这些bean定义加载到IoC容器中
-
我们可以通过basePackages等属性来细粒度的定制@ComponentScan自动扫描的范围,如果不指定,则默认Spring框架实现会从声明@ComponentScan所在类的package进行扫描。
@EnableAutoConfiguration:自动配置核心
此注解顾名思义是可以自动配置,所以应该是springboot中最为重要的注解。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
其中最重要的两个注解:1、@AutoConfigurationPackage【重点注解】2、@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)【重点注解】
@AutoConfigurationPackage
自动配置包。内部是采用了@Import,来给容器导入一个Registrar组件,程序运行到这里,会去加载启动类所在包下面的所有类
@Import:将一个组件注入容器中
@Import({Registrar.class})
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
Registrar() {
}
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
AutoConfigurationPackages.register(registry, (String[])(new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImports(metadata)).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0]));
}
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImports(metadata));
}
}
该类有一个主要方法是registerBeanDefinitions(),该方法对容器中进行了批量注册
- AnnotationMetadata(注解元数据类):该类存储了注解相关的位置、属性值等信息
- PackageImports(metadata).getPackageNames():该方法用于返回该注解所在位置的包名信息。(由此可以得到,该位置包名本质其实就是主程序所在的位置):
进入到**register()**方法的底层,发现其功能是将该包名位置下的所有组件添加到容器当中去。
由此可以得到,该注解@AutoConfigurationPackage本质上就是通过导入Register类,将@SpringBootApplication核心注解(即主程序入口)所在位置同层级包下的所有组件扫描注册到Spring容器当中去。这也就解释了为什么在建立dao、service等目录结构的时候,应该在启动程序同级目录下新建
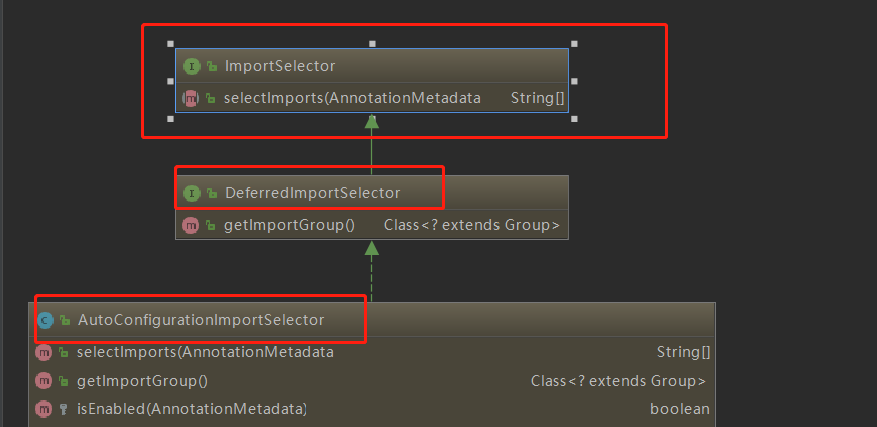
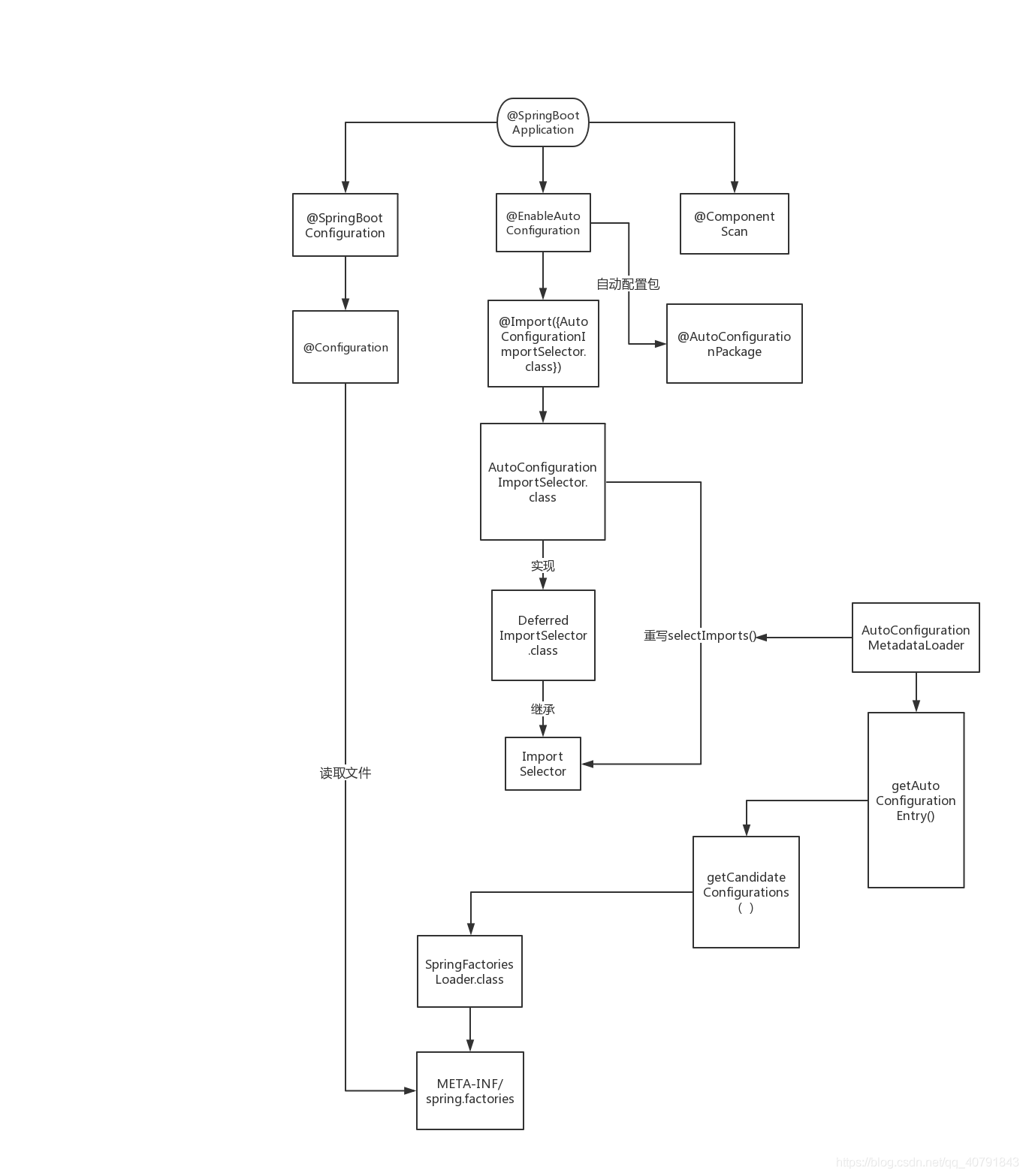
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
- 通过@Import往容器中导入注册了一个特殊类AutoConfigurationImportSelector。该类中有一个主要方法是selectImports()
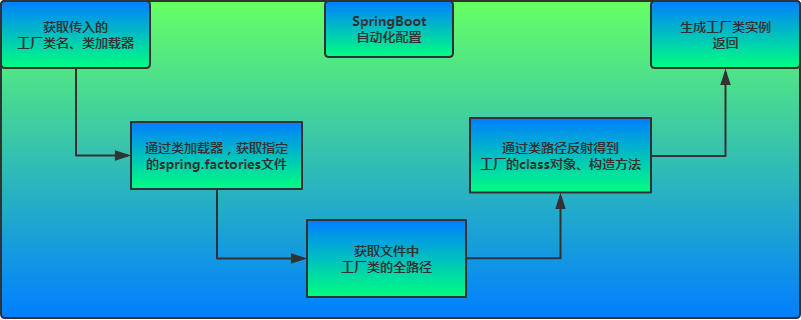
- selectImports()方法主要利用getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata)给容器中批量导入了一些组件
- getAutoConfigurationEntry方法的主要作用是调用List configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes)获取了所有的131个初始候选配置类,并将他们通过一系列筛选过滤后返回上层,最后进一步批量注册到容器中发挥作用。
- 利用工厂加载 Map<String, List> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader),得到所有的组件
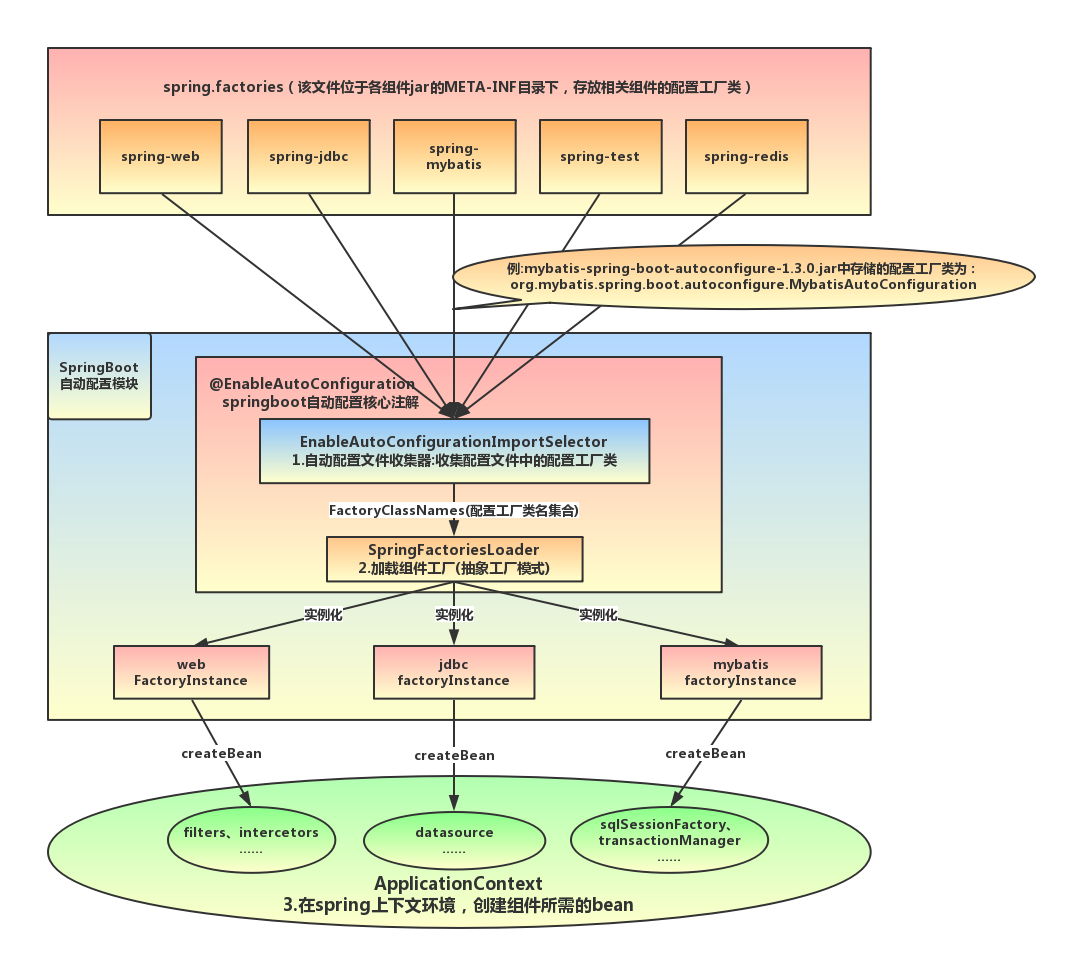
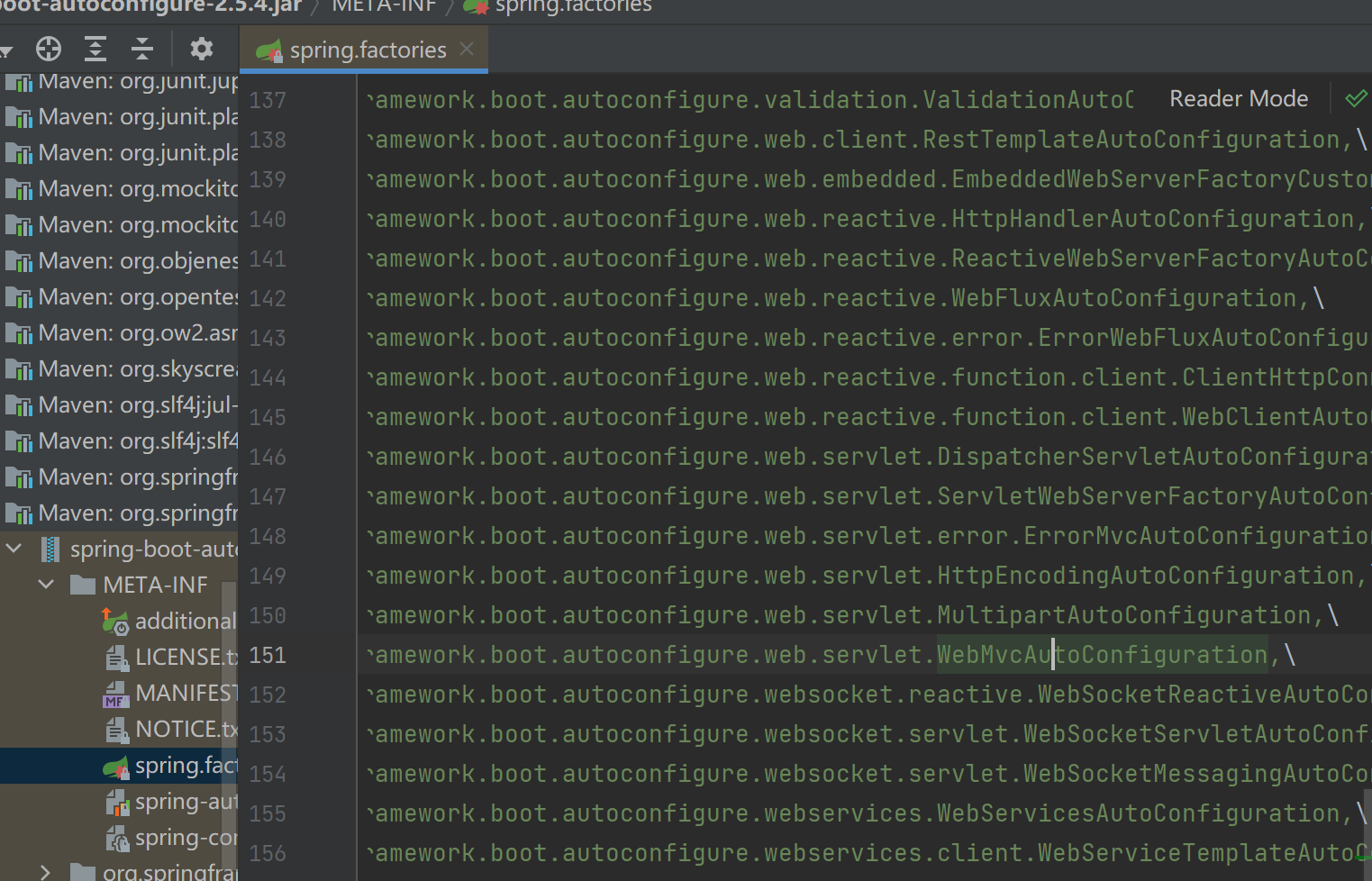
- 从META-INF/spring.factories位置来加载一个文件。默认扫描我们当前系统里面所有META-INF/spring.factories位置的文件。
我们发现在项目初始导入的每个Jar包下,都可能包含META-INF/spring.factories这个文件,文件中配置声明了一系列系统类的全类名。而其中比较核心的是spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.3.jar这个自动配置包,该文件中使用autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=声明了131个初始配置类
总结:
该注解实际上是通过导入了AutoConfigurationImportSelector这个类,初始化来自动扫描加载所有META-INF/spring.factories这个文件下写死的资源(SpringBoot帮我们配置好了),其中比较核心的是spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.3.jar这个自动配置包,该包帮我们初始化加载了131个初始配置类,帮助我们进一步完成SpringBoot的启动和配置功能!
总结
3.3.2、自动配置流程总结
3.3.3、修改默认配置
由上可以知道,自动配置会从META-INF/spring.factories加载初始配置类,初始配置类以XXXAutoConfiguration结尾,如org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,
点进去是WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java配置类
修改其默认配置可以通过application.yaml修改WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java配置类中对应的参数
如:
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /**
3.3.4、总结
一句话总结 :根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效!
- 一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;
- 这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
- 所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装着;
- 配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类
精髓
1、SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2、我们看我们需要的功能有没有在SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类当中;
3、我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件存在在其中,我们就不需要再手动配置了)
4、给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们只需要在配置文件中指定这些属性的值即可;
**xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类;**给容器中添加组件
xxxxProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性;
了解:@Conditional
了解完自动装配的原理后,我们来关注一个细节问题,自动配置类必须在一定的条件下才能生效;
@Conditional派生注解(Spring注解版原生的@Conditional作用)
作用:必须是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效;
那么多的自动配置类,必须在一定的条件下才能生效;也就是说,我们加载了这么多的配置类,但不是所有的都生效了。
我们怎么知道哪些自动配置类生效?
我们可以通过启用 debug=true属性;来让控制台打印自动配置报告,这样我们就可以很方便的知道哪些自动配置类生效;
#开启springboot的调试类
debug=true
Positive matches:(自动配置类启用的:正匹配)
Negative matches:(没有启动,没有匹配成功的自动配置类:负匹配)
Unconditional classes: (没有条件的类)
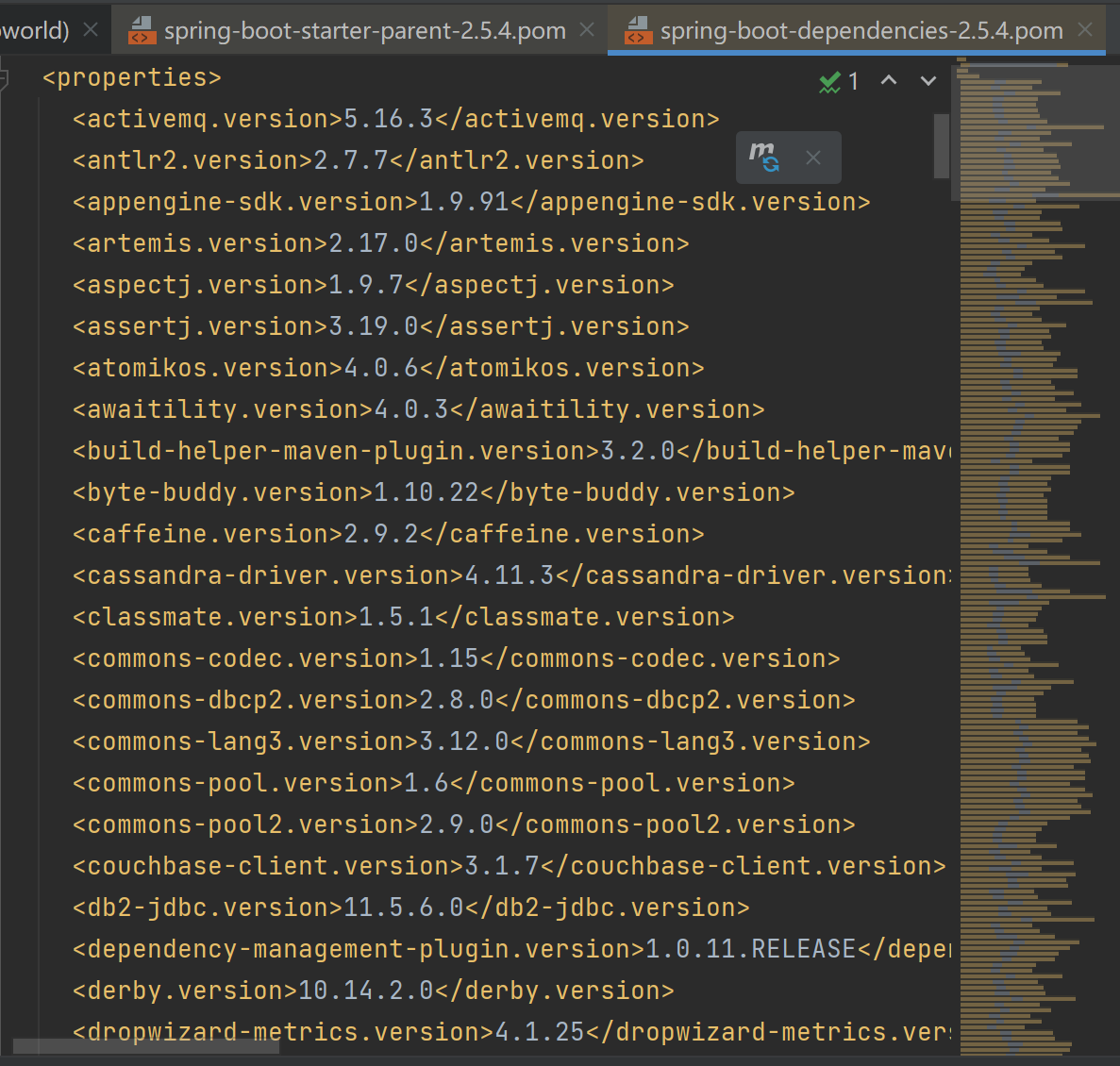
3.4、依赖管理
父工程
- springboot的父工程中,进行了资源过滤、核心依赖导入
- 在写或者引入依赖的时候,不需要指定版本
<!--有一个父项目-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
点进去,发现其父项目为:spring-boot-dependencies
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
</parent>
spring-boot-dependencies声明了很多开发中常用的jar包
所以在你pom.xml文件中引入jar的时候,如果该jar在spring-boot-dependencies中定义了版本号,那么你可以不写。如果你想使用其他的版本号,那么也可以在pom.xml中定义version,遵循就近原则。比如你想使用自定义版本号的mysql驱动,只需在pom.xml中进行定义
<properties>
<mysql.version>5.1.43</mysql.version>
</properties>
启动器
在SpringBoot项目中,我们只需要引入spring-boot-starter-web包就可以写接口并且进行访问,因为在这个starter中整合了我们之前写Spring项目时引入的spring-aop、spring-context、spring-webmvc等jar包,包括tomcat,所以SpringBoot项目不需要外部的tomcat,只需要启动application类使用内置的tomcat服务器即可。
<!--启动器-->
<!--spring-boot-starter-web中配置了spring-boot-starter启动器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-json</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.3.9</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.9</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
在SpringBoot项目中,根据官方文档,有各种场景的spring-boot-starter-*可以使用,只要引入了starter,这个场景所有常规需要的依赖就会自动引入。
所有场景启动器最底层的依赖就是spring-boot-starter,该jar包是核心启动包,包含了自动配置的支持,日志以及YAML。Core starter, including auto-configuration support, logging and YAML,这是官方对它的描述。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.5</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>5.3.9</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.yaml</groupId>
<artifactId>snakeyaml</artifactId>
<version>1.28</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
4、yaml
4.1、配置文件
SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件,配置文件的名称是固定的
- application.properties
- 语法:
key=value
- 语法:
- application.yml
- 语法:
key: 空格 value
- 语法:
配置文件的作用:修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值
4.2、yaml
以前的配置文件都是用xml配置
xml配置:
<server>
<port>8081</port>
</server>
yaml配置
server:
port: 8081
基本语法规则
同一级的字段要对齐,冒号后面要带上空格。
- 大小写敏感
- 使用缩进表示层级关系
- 缩进时不允许使用Tab键,只允许使用空格。
- 缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可
- # 表示注释,从这个字符一直到行尾,都会被解析器忽略。
YAML 支持的数据结构有三种。
- 对象:键值对的集合,又称为映射(mapping)/ 哈希(hashes) / 字典(dictionary)
- 数组:一组按次序排列的值,又称为序列(sequence) / 列表(list)
- 纯量(scalars):单个的、不可再分的值
# 普通的key-value
name: tian
# 对象
student:
name: chen
age: 18
sex: 男
class: 11
student: {name: tian,age: 18}
# 数组
# 一维数组
list:
- A
- B
- C
list: [A,B,C]
4.3、给属性赋值
实体类
Dog.class
@Component
public class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
// get,set,tostring,constuctor
}
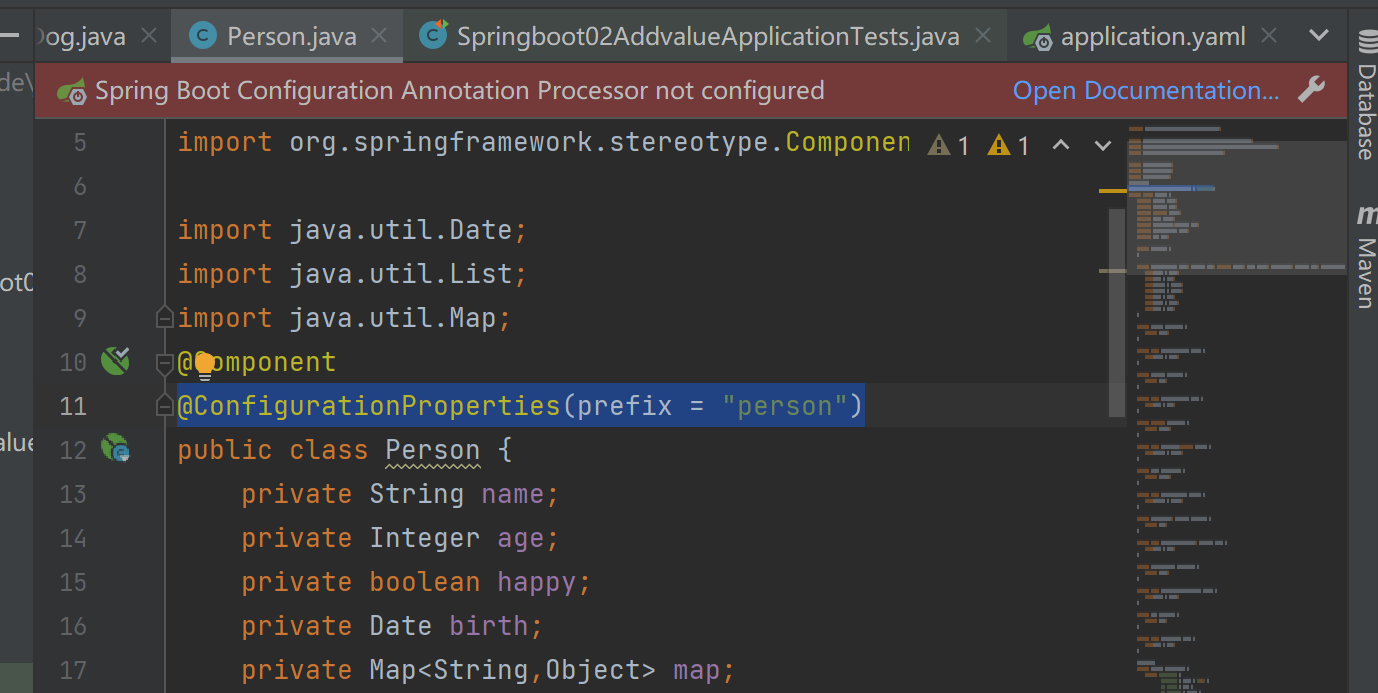
Person.class
@Component
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private boolean happy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> map;
private List<Object> list;
private Dog dog;
// get,set,tostring,constuctor
}
spring赋值
@Value(“value”)
public class Dog {
@Value("wangzai")
private String name;
@Value("1")
private Integer age;
}
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot02AddvalueApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(dog);
}
}
yaml赋值
application.yaml
person:
name: tian
age: 2
happy: false
birth: 2020-01-01
map: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
list:
- code
- jf
- fas
dog:
name: wangcai
age: 1
person.class
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
...
}
Spring Boot Configuration Annotation Processor not configured 问题解决
- 分析
它的意思是“Spring Boot配置注解执行器没有配置”,配置注解执行器的好处是什么。
配置注解执行器配置完成后,当执行类中已经定义了对象和该对象的字段后,在配置文件中对该类赋值时,便会非常方便的弹出提示信息。
- 解决
在pom.xml文件中引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
松散绑定
在yaml中写的是last-name,等同于lastName
JSR303数据校验@Validated
可以在字段增加一层过滤器验证,保证数据的合法性
- 导入依赖
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 添加注解
@Validated
public class Person {
// message为数据不合法时候的提示信息
@Email(message = "邮箱格式错误")
private String email;
}
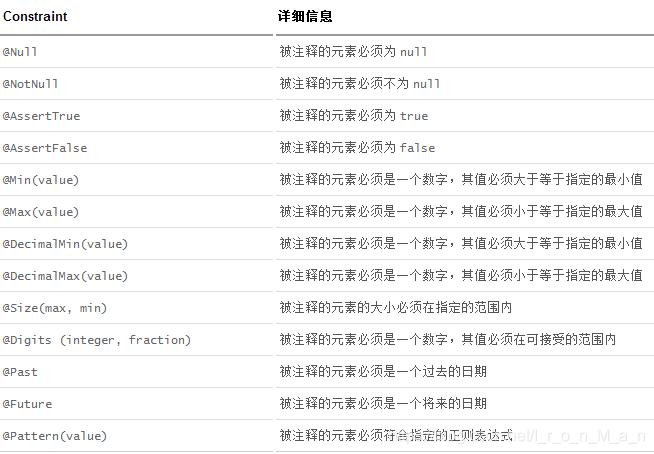
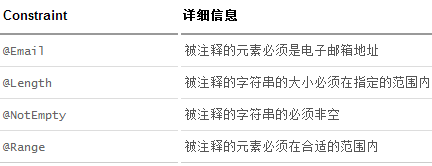
- 常见参数
- 附加
@NotNull(message="名字不能为空")
private String userName;
@Max(value=120,message="年龄最大不能查过120")
private int age;
@Email(message="邮箱格式错误")
private String email;
空检查
@Null 验证对象是否为null
@NotNull 验证对象是否不为null, 无法查检长度为0的字符串
@NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格.
@NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY.
Booelan检查
@AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true
@AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false
长度检查
@Size(min=, max=) 验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内
@Length(min=, max=) string is between min and max included.
日期检查
@Past 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前
@Future 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后
@Pattern(value) 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
5、配置文件
配置文件必须以application开头,application后面可以有其他东西,application-test
5.1、配置文件位置
配置文件可以放的位置:从上到下,优先级降低
-
file:./config/ -
file:./ -
classpath:/config/ -
classpath:/
file:./为项目根目录,即pom.xml所在的同级目录
classpath:/为src/main/resources下的目录
5.2、多环境配置
一个项目在开发环境dev、测试环境test、生产环境prod、预发布环境uat,不同的环境会有不同的配置,比如数据库的配置就不同
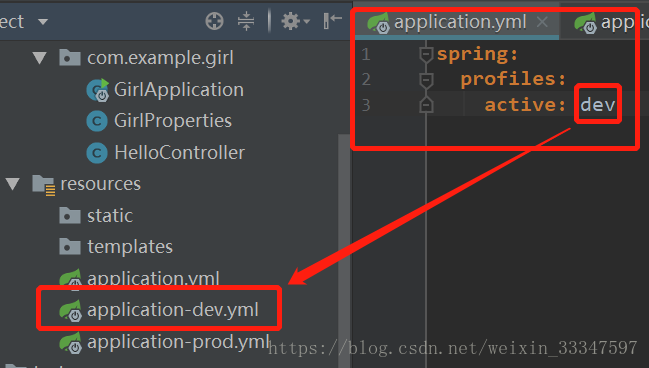
方法1:修改配置文件
这种方式的好处就是可以把公共的变量配置在application.properties文件中,不同环境需要的变量配置在不同的文件中,比如数据库信息,线程池的大小,redis信息等。
修改application.yml配置文件,具体内容如下图:
在启动服务时,服务器就会通过application.yml文件去调用application-dev.yml文件
方法2:命令启动服务,命令中带参数方式(此方式可以没有application.yml文件)
第一步:进入到项目目录下,先用maven对项目进行打包,会在target目录下生成项目的jar包
第二步:进入target目录,执行命令:java -jar 生成的jar包 --spring.profiles.active=prod
项目就会调用application-prod.yml配置文件,即以生产环境的配置要求启动服务。同理,若是开发环境,只需将prod改为dev即可。
6、SpringBoot Web开发
自动配置会从META-INF/spring.factories加载初始配置类,初始配置类以XXXAutoConfiguration结尾
springboot中webMVC开发的自动配置为org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,配置类为:WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java
6.1、静态资源路径
静态资源路径是指系统可以直接访问的路径,且路径下的所有文件均可被用户通过浏览器直接读取。
默认配置
WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java配置类中的静态资源路径设置:
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
//用户自定义后,会覆盖默认的
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
//默认路径
addResourceHandler(registry, "/webjars/**", "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (registration) -> {
registration.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
if (this.servletContext != null) {
ServletContextResource resource = new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, SERVLET_LOCATION);
registration.addResourceLocations(resource);
}
});
}
Spring Boot 对静态资源映射提供了默认配置
- 自定义:自定义后,会把下面两个默认的覆盖
- webjars(不建议使用):
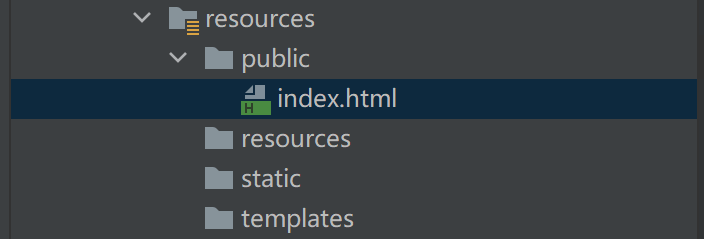
localhost:8080/webjars/ - classpath:
localhost:8080/classpath:/staticclasspath:/publicclasspath:/resourcesclasspath:/META-INF/resources
优先级:resources>static>public
注意:templates不是静态资源路径
在src/main/resources目录下新建 public、resources、static 三个目录,并分别放入 1.jpg 2.jpg 3.jpg 三张图片。然后通过浏览器分别访问:
http://localhost:8080/1.jpg
http://localhost:8080/2.jpg
http://localhost:8080/3.jpg
地址均可以正常访问,Spring Boot 默认会从 public resources static 三个目录里面查找是否存在相应的资源。
自定义资源路径
properties.yaml
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /upload/**
通过spring.mvc.static-path-pattern这种方式配置,会使Spring Boot的默认配置失效,也就是说,/public , /resources 等默认配置不能使用。 配置中配置了静态模式为/upload/**,访问时候就只能通过/upload/xx 来访问。
http://localhost:8080/upload/1.jpg
6.2、首页定制
首页可以放在public、resources、static目录下,通过localhost:8080直接访问
在templates下的只能通过controller进行访问
6.3、Thymeleaf模板引擎
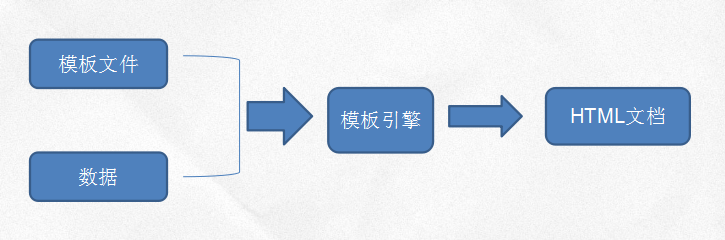
模板
模板的诞生是为了将显示与数据分离,模板技术多种多样,但其本质是将模板文件和数据通过模板引擎生成最终的HTML代码。
模板技术并不是什么神秘技术,干的是拼接字符串的体力活。模板引擎就是利用正则表达式识别模板标识,并利用数据替换其中的标识符。比如:
Hello, <%= name%>
数据是{name: '木的树'},那么通过模板引擎解析后,我们希望得到Hello, 木的树。模板的前半部分是普通字符串,后半部分是模板标识,我们需要将其中的标识符替换为表达式。模板的渲染过程如下:
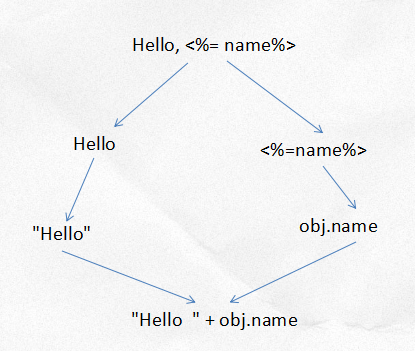
模板引擎
什么是模板引擎
模板引擎(这里特指用于Web开发的模板引擎)是为了使用户界面与业务数据(内容)分离而产生的,它可以生成特定格式的文档,用于网站的模板引擎就会生成一个标准的html文档。从字面上理解模板引擎,最重要的就是模板二字,这个意思就是做好一个模板后套入对应位置的数据,最终以html的格式展示出来,这就是模板引擎的作用。
如:Thymeleaf,FreeMarker,Enjoy,Velocity,JSP
JSP
虽然是一款功能比较强大的模板引擎,并被广大开发者熟悉,但它前后端耦合比较高。比如说前端的html页面还要手动修改成jsp页面,大大加重了工作量,而且动态和静态资源也是耦合性太高。
其次是JSP页面的效率没有HTML高,因为JSP是同步加载。而且JSP需要tomcat,但又不支持nginx等,已经跟不上时代的潮流。
综上:目前开发中已经很少用JSP了,只是我们很多时候会在碰到一些以前的框架里有用到JSP技术,但是技多不压身,推荐还是学一下(如果工作不需要,可以不学)。
Thymeleaf介绍
特点
Thymeleaf 是一个跟 Velocity、FreeMarker 类似的模板引擎,它可以完全替代 JSP 。相较与其他的模板引擎,它有如下三个极吸引人的特点:
-
Thymeleaf 在有网络和无网络的环境下皆可运行,即它可以让美工在浏览器查看页面的静态效果,也可以让程序员在服务器查看带数据的动态页面效果。这是由于它支持 html 原型,然后在 html 标签里增加额外的属性来达到模板+数据的展示方式。浏览器解释 html 时会忽略未定义的标签属性,所以 thymeleaf 的模板可以静态地运行;当有数据返回到页面时,Thymeleaf 标签会动态地替换掉静态内容,使页面动态显示。
-
Thymeleaf 开箱即用的特性。它提供标准和spring标准两种方言,可以直接套用模板实现JSTL、 OGNL表达式效果,避免每天套模板、该jstl、改标签的困扰。同时开发人员也可以扩展和创建自定义的方言。
-
Thymeleaf 提供spring标准方言和一个与 SpringMVC 完美集成的可选模块,可以快速的实现表单绑定、属性编辑器、国际化等功能。
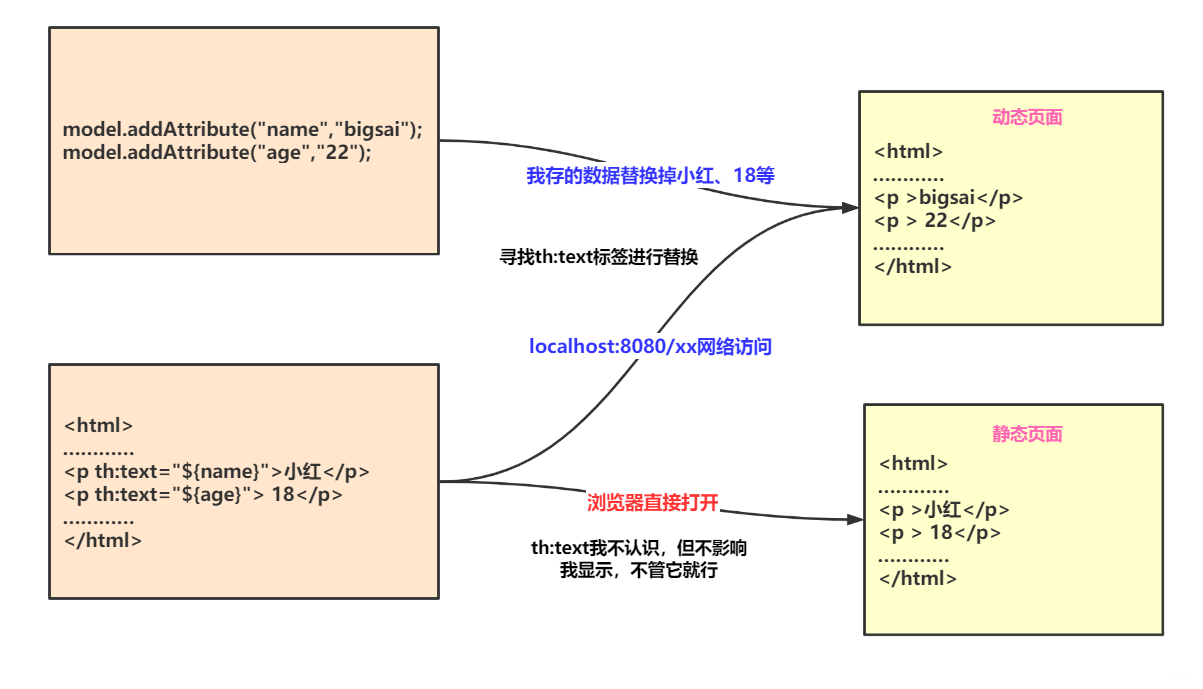
动静分离:
浏览器无法直接识别.jsp文件,需要借助网络(服务端)才能进行访问;而Thymeleaf用html做模板可以直接在浏览器中打开。开发者充分考虑html页面特性,将Thymeleaf的语法通过html的标签属性来定义完成,这些标签属性不会影响html页面的完整性和显示。如果通过后台服务端访问页面服务端会寻找这些标签将服务端对应的数据替换到相应位置实现动态页面!大体区别可以参照下图:
上图的意思就是如果直接打开这个html那么浏览器会对th等标签忽视而显示原始的内容。如果通过服务端访问那么服务端将先寻找th标签将服务端储存的数据替换到对应位置。具体效果可以参照下图,下图即为一个动静结合的实例。
使用Thymeleaf
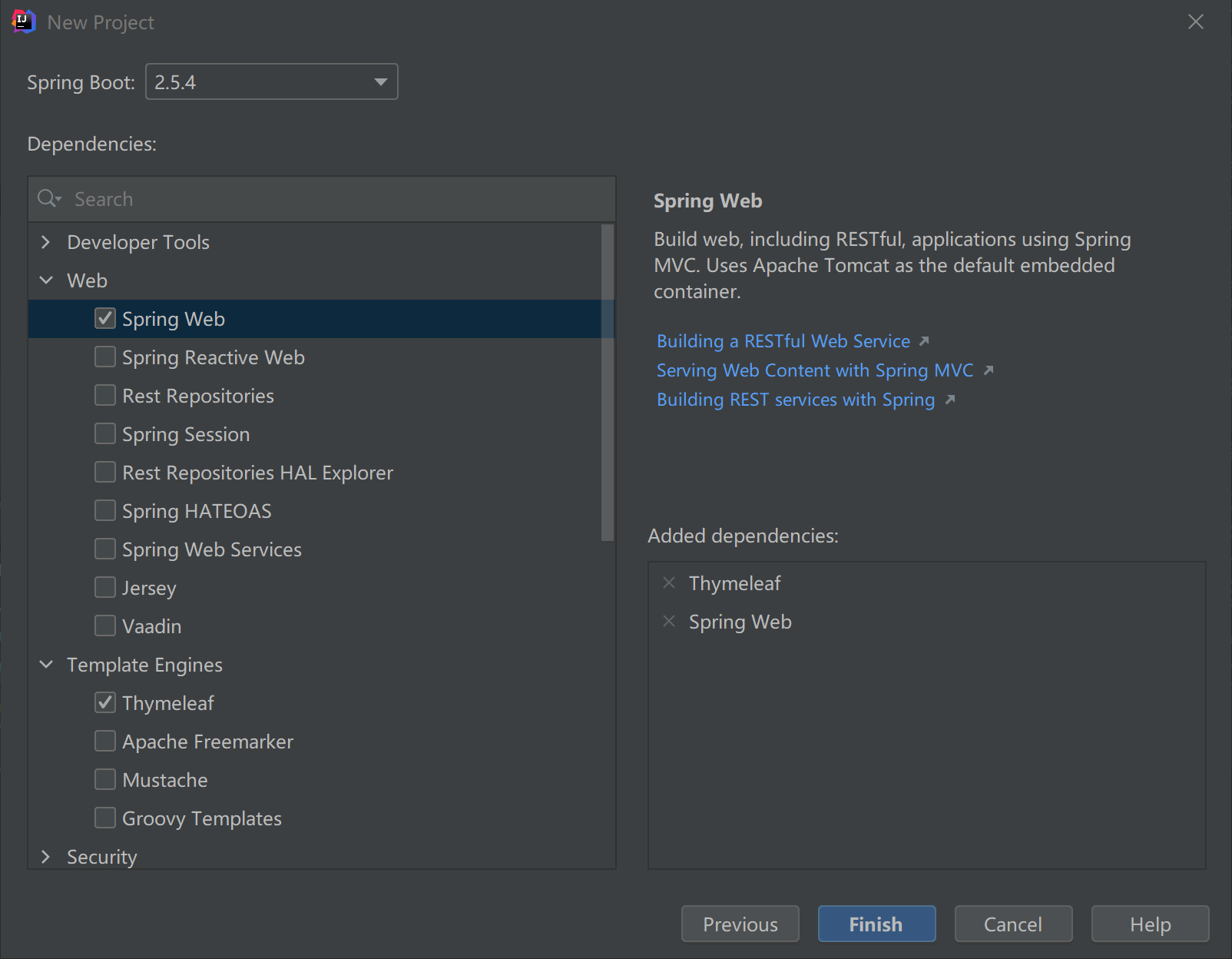
对于构建一个完整程序,创建第一个Thymeleaf程序需要以下几个步骤:
- 创建程序,添加依赖
- 编写Controller
- 编写Thymeleaf页面:需要放在
templates目录下 - 访问页面
创建程序,添加依赖
- 方法1:在创建程序的时候,勾选其中Web 模块的Spring web依赖以及Template 模块的Thymeleaf依赖
- 方法2:在pom.xml中添加以下依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
编写controller
@Controller
public class ThymeleafController {
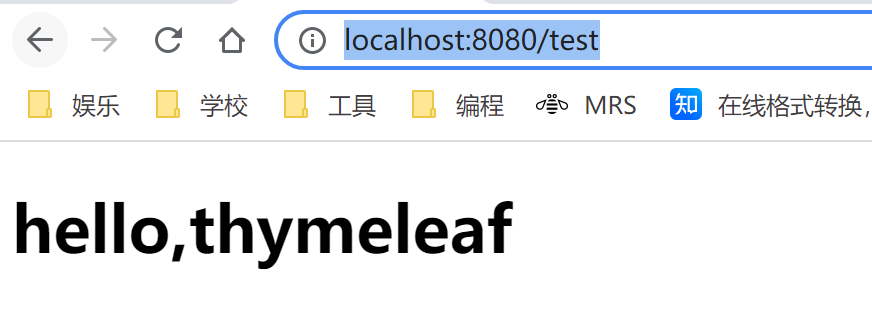
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test1(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("msg", "hello,thymeleaf");
return "test";
}
}
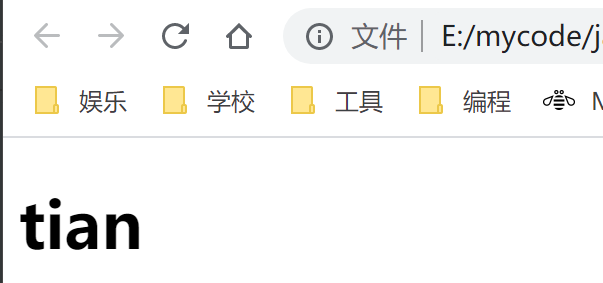
编写Thymeleaf页面
咱们在项目的resources目录下的templates文件夹下面创建一个叫index.html的文件,咱们在这个html文件中的<html>标签修改为<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">这样在Thymeleaf中就可以使用Thymeleaf的语法和规范啦。
test.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1><div th:text="${msg}">tian</div> </h1>
</body>
</html>
浏览器测试
- 直接打开页面
- 通过服务端访问
会进行动态替换
thymeleaf语法
标签
Thymeleaf通过特殊的标签来寻找属于Thymeleaf的部分,并渲染该部分内容。Thymeleaf也主要通过标签来识别替换对应位置内容,Thymeleaf标签有很多很多,功能也很丰富,这里列举一些比较常用的标签如下:
| 标签 | 作用 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| th:id | 替换id | <input th:id="${user.id}"/> |
| th:text | 文本替换 | <p text:="${user.name}">bigsai</p> |
| th:utext | 支持html的文本替换 | <p utext:="${htmlcontent}">content</p> |
| th:object | 替换对象 | <div th:object="${user}"></div> |
| th:value | 替换值 | <input th:value="${user.name}" > |
| th:each | 迭代 | <tr th:each="student:${user}" > |
| th:href | 替换超链接 | <a th:href="@{index.html}">超链接</a> |
| th:src | 替换资源 | <script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{index.js}"></script> |
链接表达式@{…}
上面我们已经学习到Thymeleaf是一个基于html的模板引擎,但是我们还是需要加入特定标签来声明和使用Thymeleaf的语法。我们需要在Thymeleaf的头部加Thymeleaf标识:
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
在Thymeleaf 中,如果想引入链接比如link,href,src,需要使用@{资源地址}引入资源。其中资源地址可以static目录下的静态资源,也可以是互联网中的绝对资源。
引入css
<link rel="stylesheet" th:href="@{index.css}">
引入JavaScript:
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{index.js}"></script>
超链接:
<a th:href="@{index.html}">超链接</a>
变量表达式: ${...}
在Thymeleaf中可以通过${…}进行取值,这点和ONGL表达式语法一致。
取普通字符串:
如果在controller中的Model直接存储某字符串,我们可以直接${对象名}进行取值。完整代码如下:
<h2>普通字符串</h2>
<table border="0">
<tr>
<td th:text="'我的名字是:'+${name}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
取JavaBean对象:
取JavaBean对象也很容易,因为JavaBean自身有一些其他属性,所以咱们就可以使用${对象名.对象属性}或者${对象名['对象属性']}来取值,这和JavaScript语法是不是很相似呢!除此之外,如果该JavaBean如果写了get方法,咱们也可以通过get方法取值例如${对象.get方法名}完整代码如下:
<h2>JavaBean对象</h2>
<table bgcolor="#ffe4c4" border="1">
<tr>
<td>介绍</td>
<td th:text="${user.name}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>年龄</td>
<td th:text="${user['age']}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>介绍</td>
<td th:text="${user.getDetail()}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
取List集合(each):
因为List集合是个有序列表,里面内容可能不止一个,你需要遍历List对其中对象取值,而遍历需要用到标签:th:each,具体使用为 <tr th:each="item:${userlist}">,其中item就相当于遍历每一次的对象名,在下面的作用域可以直接使用,而userlist就是你在Model中储存的List的名称。完整的代码为:
<h2>List取值</h2>
<table bgcolor="#ffe4c4" border="1">
<tr th:each="item:${userlist}">
<td th:text="${item}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
直接取Map:
很多时候我们不存JavaBean而是将一些值放入Map中,再将Map存在Model中,我们就需要对Map取值,对于Map取值你可以${Map名['key']}来进行取值。也可以通过${Map名.key}取值,当然你也可以使用${map.get('key')}(java语法)来取值,完整代码如下:
<h2>Map取值</h2>
<table bgcolor="#8fbc8f" border="1">
<tr>
<td>place:</td>
<td th:text="${map.get('place')}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>feeling:</td>
<td th:text="${map['feeling']}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
遍历Map:
如果说你想遍历Map获取它的key和value那也是可以的,这里就要使用和List相似的遍历方法,使用th:each="item:${Map名}"进行遍历,在下面只需使用item.key和item.value即可获得值。完整代码如下:
<h2>Map遍历</h2>
<table bgcolor="#ffe4c4" border="1">
<tr th:each="item:${map}">
<td th:text="${item.key}"></td>
<td th:text="${item.value}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
选择表达式
- if-then:
(if) ? (then) - if-then-else:
(if) ? (then) : (else) - default :
(value) ?: (defaultvalue)
选择变量表达式: *{...}
变量表达式不仅可以写成${...},而且还可以写成*{...}。
但是,有一个重要的区别:星号语法对选定对象而不是整个上下文评估表达式。也就是说,只要没有选定的对象,美元(${…})和星号(*{...})的语法就完全一样。
什么是选定对象?使用th:object属性的表达式的结果。就可以选定对象,具体实例如下:
<div th:object="${user}">
<p>Name: <span th:text="*{name}">赛</span>.</p>
<p>Age: <span th:text="*{age}">18</span>.</p>
<p>Detail: <span th:text="*{detail}">好好学习</span>.</p>
</div>
当然*{…}也可和${…}混用。上面的代码如果不使用选定对象,完全等价于:
<div >
<p>Name: <span th:text="*{user.name}">赛</span>.</p>
<p>Age: <span th:text="${user.age}">18</span>.</p>
<p>Detail: <span th:text="${user.detail}">好好学习</span>.</p>
</div>
消息表达: #{...}
文本外部化是从模板文件中提取模板代码的片段,以便可以将它们保存在单独的文件(通常是.properties文件)中,文本的外部化片段通常称为“消息”。通俗易懂的来说#{…}语法就是用来读取配置文件中数据的。在Thymeleaf你可以使用#{...}语法获取消息,具体实例代码如下:
首先在templates目录下建立home.properties中写入以下内容:
bigsai.nane=bigsai
bigsai.age=22
province=Jiang Su
在application.properties中加入以下内容:
spring.messages.basename=templates/home
这样我们就可以在Thymeleaf中读取配置的文件了,完整代码如下:
<h2>消息表达</h2>
<table bgcolor="#ffe4c4" border="1">
<tr>
<td>name</td>
<td th:text="#{bigsai.name}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>年龄</td>
<td th:text="#{bigsai.age}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>province</td>
<td th:text="#{province}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
抽取公共页面
网页中很多具有公共的部分,可以把公共的部分抽取出来,放在resources/commons/commons.html下
- 定义公共部分
<p th:fragment="xxx">
//公共部分
</p>
- 使用公共部分
<div th:insert="~{commons/commons::xxx}"></div>
或者用th:replace
6.4、扩展SpringMVC
扩展
Springboot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的,如果有就用用户自己配置的,如果没有就用自动配置的,如果有些组件可以存在多个,比如视图解析器,就将用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来
-
编写一个**@Configuration注解类**,类型要为**WebMvcConfigurer**,还**不能标注@EnableWebMve**注解,一般放在config包下、
-
重写相应的方法
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//视图跳转
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/tiaozhuan").setViewName("test");
}
}
如上,重写了addViewControllers方法,当浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080/tiaozhuan时,会跳转到templates下的test.html页面
7、员工管理系统
7.1、准备工作
资源下载
下载完成后放置资源
数据
7.2、首页
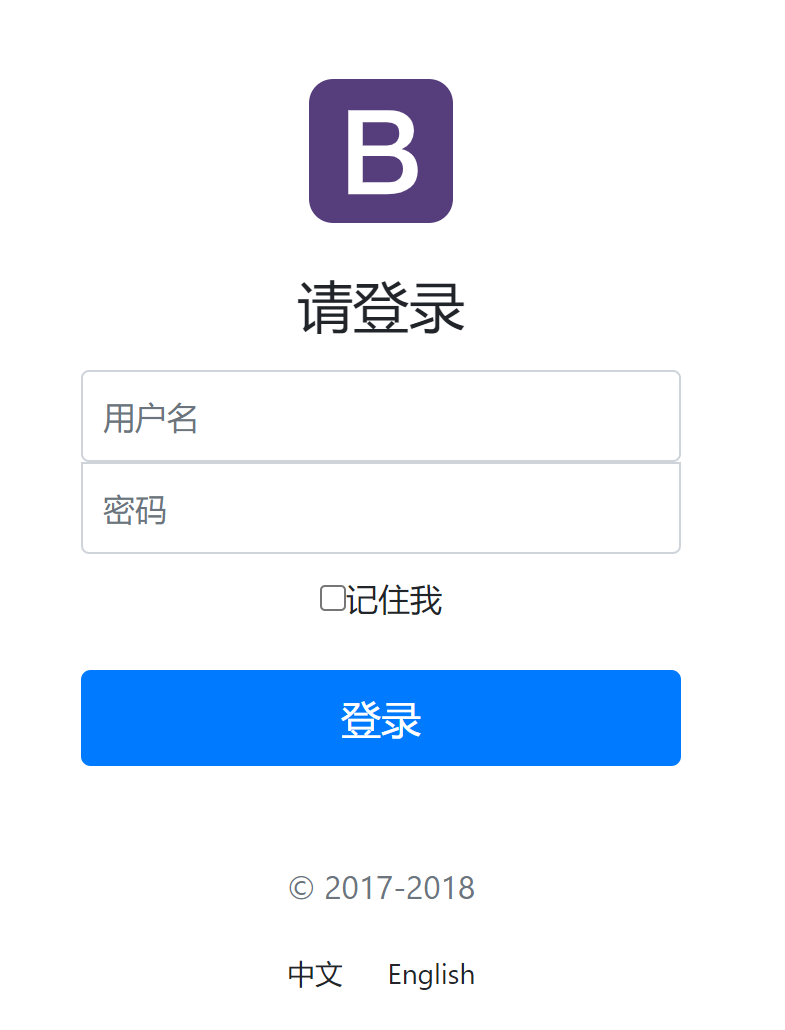
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">
<meta name="description" content="">
<meta name="author" content="">
<title>Signin Template for Bootstrap</title>
<!-- Bootstrap core CSS -->
<link href="/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- Custom styles for this template -->
<link href="asserts/css/signin.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body class="text-center">
<form class="form-signin" action="dashboard.html">
<img class="mb-4" src="/img/bootstrap-solid.svg" alt="" width="72" height="72">
<h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal">Please sign in</h1>
<label class="sr-only">Username</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="Username" required="" autofocus="">
<label class="sr-only">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" placeholder="Password" required="">
<div class="checkbox mb-3">
<label>
<input type="checkbox" value="remember-me"> Remember me
</label>
</div>
<button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit">Sign in</button>
<p class="mt-5 mb-3 text-muted">© 2017-2018</p>
<a class="btn btn-sm">中文</a>
<a class="btn btn-sm">English</a>
</form>
</body>
</html>
首页访问
首页index.html在templates目录下,不能直接访问
通过下面两种方法设置后,可以通过http://localhost:8080和http://localhost:8080/index.html访问
- 方法1:通过增加controller
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping({"/","/index.html"})
public String index() {
return "index";
}
}
- 方法2:通过扩展springmvc
@Configuration
public class MyMvcCfonfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("index");
}
}
首页Thymeleaf
所有页面的静态资源都需要使用thymeleaf接管:th:href=“@{}”
使用thymeleaf语法对首页中的链接进行更改
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
# 略
<!-- Bootstrap core CSS -->
<link th:href="@{/css/bootstrap.min.css}" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- Custom styles for this template -->
<link th:href="@{/css/signin.css}" rel="stylesheet">
# 略
<img class="mb-4" th:src="@{/img/bootstrap-solid.svg}" alt="" width="72" height="72">
7.3、页面国际化
中英文语言切换
设置idea
设置为utf-8
编写国际化配置文件
- login.properties
login.btn=登录
login.password=密码
login.remember=记住我
login.tip=请登录
login.username=用户名
- login_en_US.properties
login.btn=sign in
login.password=password
login.remember=remember me
login.tip=please sign in
login.username=username
- login_zh_CN.properties
login.btn=登录
login.password=密码
login.remember=记住我
login.tip=请登录
login.username=用户名
配置文件位置
国际化自动配置类:MessageSourceAutoConfiguration.class
在application.properties中配置
# 配置g国际化文件位置
spring.messages.basename=i18n.login
页面中设置国际化消息Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf语法:th:text=“#{}”
<!--原来的-->
<h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal">Please sign in</h1>
<!--改后-->
<h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal" th:text="#{login.tip}">Please sign in</h1>
<!--其他类似-->
语言切换
国际化语言的切换主要是因为有一个区域信息解析器在其作用。
是根据HttpServletRequest中的locale属性来判定启用哪个语言文件的。
我们的需求是通过点击链接来切换语言,那么我们可以自定义一个区域信息解析器来替代这个默认的解析器。
- 首先,配置类扩展mvc
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new NativeLocaleResolver();
}
protected static class NativeLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver{
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
String language = request.getParameter("language");
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(language)){
String[] split = language.split("_");
locale = new Locale(split[0],split[1]);
}
return locale;
}
@Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) {
}
}
- 编写页面
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(language='zh_CN')}">中文</a>
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(language='en_US')}">English</a>
7.4、登录
index.html
<form class="form-signin" th:action="@{/user/login}">
<h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal" th:text="#{login.tip}">Please sign in</h1>
//显示提示信息msg
<p style="color: red" th:text="${msg}"></p>
controller
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@RequestMapping("/user/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username,
@RequestParam("password") String password,
Model model) {
//判断,本来应该接受参数,并且和数据库中的用户名密码比较再进行跳转
if ("admin".equals(username) && "123123".equals(password)) {
return "dashboard";
} else {
model.addAttribute("msg", "用户名或者密码错误");
return "index";
}
}
}
7.5、登录拦截
编写拦截器
public class LoginHandleInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
//登录之后有用户的session
Object loginUser = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser");
if (loginUser == null) {
request.setAttribute("msg", "请登录后再试");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html").forward(request, response);
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
扩展mvc
@Configuration
public class MyMvcCfonfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/main.html").setViewName("dashboard");
}
//国际化
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new NativeLocaleResolver();
}
protected static class NativeLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver{
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
String language = request.getParameter("language");
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(language)){
String[] split = language.split("_");
locale = new Locale(split[0],split[1]);
}
return locale;
}
@Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) {
}
}
//扩展mvc 添加拦截器
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandleInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**")
.excludePathPatterns("/index.html","/","/user/login","/css/**","/img/**","/js/**");
}
}
8、写网站
- 前端:页面的样子
- 设计数据库(难点)
- 前端独立运行,独立化工程
- 数据接口对接:json、对象all in one
- 前后端联调测试
写前端
- 模板:别人写好的,拿过来改
- 框架:组件,自己手动组合拼接:BootStrap、Layui、semantic-ui
准备
- 一套自己熟悉的后台模板:工作必要,x-admin
- 前端界面:至少自己能够通过前端框架组合出来一个网站页面
- 让网站能独立运行
9、SpringBoot整合JDBC
9.1、SpringData简介
对于数据访问层,无论是 SQL(关系型数据库) 还是 NOSQL(非关系型数据库),Spring Boot 底层都是采用 Spring Data 的方式进行统一处理。
Spring Boot 底层都是采用 Spring Data 的方式进行统一处理各种数据库,Spring Data 也是 Spring 中与 Spring Boot、Spring Cloud 等齐名的知名项目。
数据库相关的启动器 :可以参考官方文档
9.2、整合JDBC
简单测试
创建项目
在SQL中勾选JDBC API和MySQL Driver
pop.xml中会自动引入依赖
编写yaml配置文件连接数据库
application.yaml
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?uerUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
简单测试
配置完这一些东西后,我们就可以直接去使用了,因为SpringBoot已经默认帮我们进行了自动配置;
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot05JdbcApplicationTests {
//获取数据源
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
void contextLoads() throws SQLException {
//查看默认的数据源,输出class com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass());
//获取数据库链接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
//关闭
connection.close();
}
}
结果:我们可以看到他默认给我们配置的数据源为 : class com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource , 我们并没有手动配置
我们来全局搜索一下,找到数据源的所有自动配置都在 :DataSourceAutoConfiguration文件:
@Import(
{Hikari.class, Tomcat.class, Dbcp2.class, Generic.class, DataSourceJmxConfiguration.class}
)
protected static class PooledDataSourceConfiguration {
protected PooledDataSourceConfiguration() {
}
}
这里导入的类都在 DataSourceConfiguration 配置类下,可以看出 Spring Boot 2.2.5 默认使用HikariDataSource 数据源,而以前版本,如 Spring Boot 1.5 默认使用 org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource 作为数据源;
HikariDataSource 号称 Java WEB 当前速度最快的数据源,相比于传统的 C3P0 、DBCP、Tomcat jdbc 等连接池更加优秀;
可以使用 spring.datasource.type 指定自定义的数据源类型,值为 要使用的连接池实现的完全限定名。
JDBCTemplate
有了数据源(com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource),然后可以拿到数据库连接(java.sql.Connection),有了连接,就可以使用原生的 JDBC 语句来操作数据库;
2、即使不使用第三方第数据库操作框架,如 MyBatis等,Spring 本身也对原生的JDBC 做了轻量级的封装,即JdbcTemplate。
3、数据库操作的所有 CRUD 方法都在 JdbcTemplate 中。
4、Spring Boot 不仅提供了默认的数据源,同时默认已经配置好了 JdbcTemplate 放在了容器中,程序员只需自己注入即可使用
5、JdbcTemplate 的自动配置是依赖 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc 包下的 JdbcTemplateConfiguration 类
JdbcTemplate主要提供以下几类方法:
- execute方法:可以用于执行任何SQL语句,一般用于执行DDL语句;
- update方法及batchUpdate方法:update方法用于执行新增、修改、删除等语句;batchUpdate方法用于执行批处理相关语句;
- query方法及queryForXXX方法:用于执行查询相关语句;
- call方法:用于执行存储过程、函数相关语句。
使用数据库,编写controller
@RestController
public class JDBCController {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
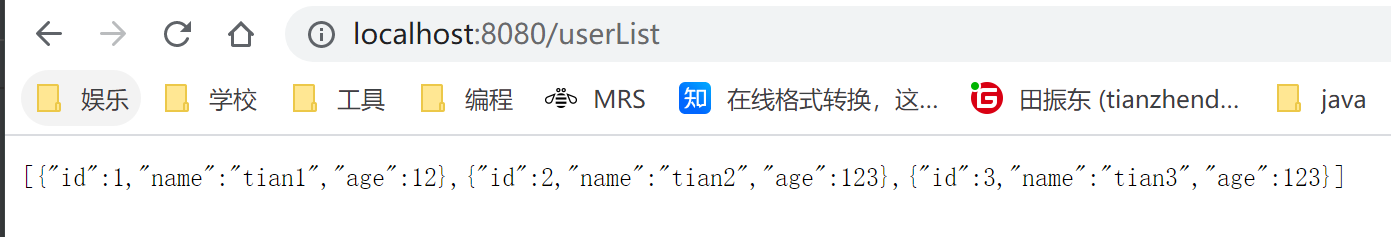
//查询数据库中的信息,由于没有实体类,因此使用map
@GetMapping("/userList")
public List<Map<String,Object>> userList() {
String sql = "select * from user";
List<Map<String, Object>> lists = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
return lists;
}
//增加
//会自动提交事务
@GetMapping("/add")
public void addUser() {
String sql = "insert into mybatis.user(id,name,age) values (4,'tian','34')";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql);
}
}
10、整合Druid
简介
Java程序很大一部分要操作数据库,为了提高性能操作数据库的时候,又不得不使用数据库连接池。
Druid 是阿里巴巴开源平台上一个数据库连接池实现,结合了 C3P0、DBCP 等 DB 池的优点,同时加入了日志监控。
Druid 可以很好的监控 DB 池连接和 SQL 的执行情况,天生就是针对监控而生的 DB 连接池。
Druid已经在阿里巴巴部署了超过600个应用,经过一年多生产环境大规模部署的严苛考验。
Spring Boot 2.0 以上默认使用 Hikari 数据源,可以说 Hikari 与 Driud 都是当前 Java Web 上最优秀的数据源,我们来重点介绍 Spring Boot 如何集成 Druid 数据源,如何实现数据库监控。
Github地址:https://github.com/alibaba/druid/
com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 基本配置参数如下:
配置数据源
1、添加上 Druid 数据源依赖。
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/druid -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.21</version>
</dependency>
2、切换数据源;之前已经说过 Spring Boot 2.0 以上默认使用 com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource 数据源,但可以 通过 spring.datasource.type 指定数据源。
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource # 自定义数据源
3、数据源切换之后,在测试类中注入 DataSource,然后获取到它,输出一看便知是否成功切换;
4、切换成功!既然切换成功,就可以设置数据源连接初始化大小、最大连接数、等待时间、最小连接数 等设置项;可以查看源码
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
#?serverTimezone=UTC解决时区的报错
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定
#druid 数据源专有配置
initialSize: 5
minIdle: 5
maxActive: 20
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
#配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入
#如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority
#则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j
filters: stat,wall,log4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
5、导入Log4j 的依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
6、现在需要程序员自己为 DruidDataSource 绑定全局配置文件中的参数,再添加到容器中,而不再使用 Spring Boot 的自动生成了;我们需要 自己添加 DruidDataSource 组件到容器中,并绑定属性;
@Configurationpublic class DruidConfig { /* 将自定义的 Druid数据源添加到容器中,不再让 Spring Boot 自动创建 绑定全局配置文件中的 druid 数据源属性到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource从而让它们生效 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource"):作用就是将 全局配置文件中 前缀为 spring.datasource的属性值注入到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 的同名参数中 */ @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") @Bean public DataSource druidDataSource() { return new DruidDataSource(); }}
7、去测试类中测试一下;看是否成功!
@SpringBootTestclass SpringbootDataJdbcApplicationTests { //DI注入数据源 @Autowired DataSource dataSource; @Test public void contextLoads() throws SQLException { //看一下默认数据源 System.out.println(dataSource.getClass()); //获得连接 Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection(); System.out.println(connection); DruidDataSource druidDataSource = (DruidDataSource) dataSource; System.out.println("druidDataSource 数据源最大连接数:" + druidDataSource.getMaxActive()); System.out.println("druidDataSource 数据源初始化连接数:" + druidDataSource.getInitialSize()); //关闭连接 connection.close(); }}
输出结果 :可见配置参数已经生效!
配置Druid数据源监控
Druid 数据源具有监控的功能,并提供了一个 web 界面方便用户查看,类似安装 路由器 时,人家也提供了一个默认的 web 页面。
所以第一步需要设置 Druid 的后台管理页面,比如 登录账号、密码 等;配置后台管理;
//配置 Druid 监控管理后台的Servlet;//内置 Servlet 容器时没有web.xml文件,所以使用 Spring Boot 的注册 Servlet 方式@Beanpublic ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet() { ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*"); // 这些参数可以在 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet // 的父类 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.ResourceServlet 中找到 Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>(); initParams.put("loginUsername", "admin"); //后台管理界面的登录账号 initParams.put("loginPassword", "123456"); //后台管理界面的登录密码 //后台允许谁可以访问 //initParams.put("allow", "localhost"):表示只有本机可以访问 //initParams.put("allow", ""):为空或者为null时,表示允许所有访问 initParams.put("allow", ""); //deny:Druid 后台拒绝谁访问 //initParams.put("kuangshen", "192.168.1.20");表示禁止此ip访问 //设置初始化参数 bean.setInitParameters(initParams); return bean;}
配置完毕后,我们可以选择访问 :http://localhost:8080/druid/login.html
进入之后
配置 Druid web 监控 filter 过滤器
//配置 Druid 监控 之 web 监控的 filter//WebStatFilter:用于配置Web和Druid数据源之间的管理关联监控统计@Beanpublic FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter() { FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean(); bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter()); //exclusions:设置哪些请求进行过滤排除掉,从而不进行统计 Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>(); initParams.put("exclusions", "*.js,*.css,/druid/*,/jdbc/*"); bean.setInitParameters(initParams); //"/*" 表示过滤所有请求 bean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*")); return bean;}
平时在工作中,按需求进行配置即可,主要用作监控!
11、整合Mybatis
官方文档:http://mybatis.org/spring-boot-starter/mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure/
Maven仓库地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis.spring.boot/mybatis-spring-boot-starter/2.1.1
导入Mybatis依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.1.1</version></dependency>
配置数据库连接信息(不变)
spring: datasource: username: root password: 123456 #?serverTimezone=UTC解决时区的报错 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource #Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定 #druid 数据源专有配置 initialSize: 5 minIdle: 5 maxActive: 20 maxWait: 60000 timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000 minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000 validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL testWhileIdle: true testOnBorrow: false testOnReturn: false poolPreparedStatements: true #配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入 #如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority #则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j filters: stat,wall,log4j maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20 useGlobalDataSourceStat: true connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
测试数据库是否连接成功
创建实体类
Department.java
@Data@NoArgsConstructor@AllArgsConstructorpublic class Department { private Integer id; private String departmentName;}
创建mapper目录以及对应的 Mapper 接口
DepartmentMapper.java
//@Mapper : 表示本类是一个 MyBatis 的 Mapper@Mapper@Repositorypublic interface DepartmentMapper { // 获取所有部门信息 List<Department> getDepartments(); // 通过id获得部门 Department getDepartment(Integer id);}
对应的Mapper映射文件:编写sql
现在一般放在resources/mybatis目录下
DepartmentMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="com.kuang.mapper.DepartmentMapper"> <select id="getDepartments" resultType="Department"> select * from department; </select> <select id="getDepartment" resultType="Department" parameterType="int"> select * from department where id = #{id}; </select></mapper>
maven配置资源过滤问题
<resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/java</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>true</filtering> </resource></resources>
业务层调用dao层
略
编写部门的 DepartmentController 进行测试
正常应该是调用service,这里略去了service层
@RestControllerpublic class DepartmentController { /* 整场应该是调用service,这里略去service层 */ @Autowired DepartmentMapper departmentMapper; // 查询全部部门 @GetMapping("/getDepartments") public List<Department> getDepartments(){ return departmentMapper.getDepartments(); } // 查询全部部门 @GetMapping("/getDepartment/{id}") public Department getDepartment(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){ return departmentMapper.getDepartment(id); } }
12、SpringSecurity
12.1、安全简介
在 Web 开发中,安全一直是非常重要的一个方面。安全虽然属于应用的非功能性需求,但是应该在应用开发的初期就考虑进来。如果在应用开发的后期才考虑安全的问题,就可能陷入一个两难的境地:一方面,应用存在严重的安全漏洞,无法满足用户的要求,并可能造成用户的隐私数据被攻击者窃取;另一方面,应用的基本架构已经确定,要修复安全漏洞,可能需要对系统的架构做出比较重大的调整,因而需要更多的开发时间,影响应用的发布进程。因此,从应用开发的第一天就应该把安全相关的因素考虑进来,并在整个应用的开发过程中。
Spring 是一个非常流行和成功的 Java 应用开发框架。Spring Security 基于 Spring 框架,提供了一套 Web 应用安全性的完整解决方案。一般来说,Web 应用的安全性包括**用户认证(Authentication)和用户授权(Authorization)**两个部分。
- 用户认证指的是验证某个用户是否为系统中的合法主体,也就是说用户能否访问该系统。用户认证一般要求用户提供用户名和密码。系统通过校验用户名和密码来完成认证过程。
- 用户授权指的是验证某个用户是否有权限执行某个操作。在一个系统中,不同用户所具有的权限是不同的。比如对一个文件来说,有的用户只能进行读取,而有的用户可以进行修改。一般来说,系统会为不同的用户分配不同的角色,而每个角色则对应一系列的权限。
市面上存在比较有名的:
- Shiro
- **Spring Security **
12.2、Spring Security
概述
对于上面提到的两种应用情景,Spring Security 框架都有很好的支持。
- 在用户认证方面,Spring Security 框架支持主流的认证方式,包括 HTTP 基本认证、HTTP 表单验证、HTTP 摘要认证、OpenID 和 LDAP 等。
- 在用户授权方面,Spring Security 提供了基于角色的访问控制和访问控制列表(Access Control List,ACL),可以对应用中的领域对象进行细粒度的控制。
Spring Security是一个功能强大且高度可定制的身份验证和访问控制框架。它实际上是保护基于spring的应用程序的标准。
Spring Security是一个框架,侧重于为Java应用程序提供身份验证和授权。与所有Spring项目一样,Spring安全性的真正强大之处在于它可以轻松地扩展以满足定制需求
Spring Security 是针对Spring项目的安全框架,也是Spring Boot底层安全模块默认的技术选型,他可以实现强大的Web安全控制,对于安全控制,我们仅需要引入 spring-boot-starter-security 模块,进行少量的配置,即可实现强大的安全管理!
记住几个类:
- WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter:自定义Security策略
- AuthenticationManagerBuilder:自定义认证策略
- @EnableWebSecurity:开启WebSecurity模式
Spring Security的两个主要目标是 “认证” 和 “授权”(访问控制)。
“认证”(Authentication)
身份验证是关于验证您的凭据,如用户名/用户ID和密码,以验证您的身份。
身份验证通常通过用户名和密码完成,有时与身份验证因素结合使用。
“授权” (Authorization)
授权发生在系统成功验证您的身份后,最终会授予您访问资源(如信息,文件,数据库,资金,位置,几乎任何内容)的完全权限。
这个概念是通用的,而不是只在Spring Security 中存在。
环境搭建
- 新建springboot项目,导入web和thymeleaf
- 导入/新建页面
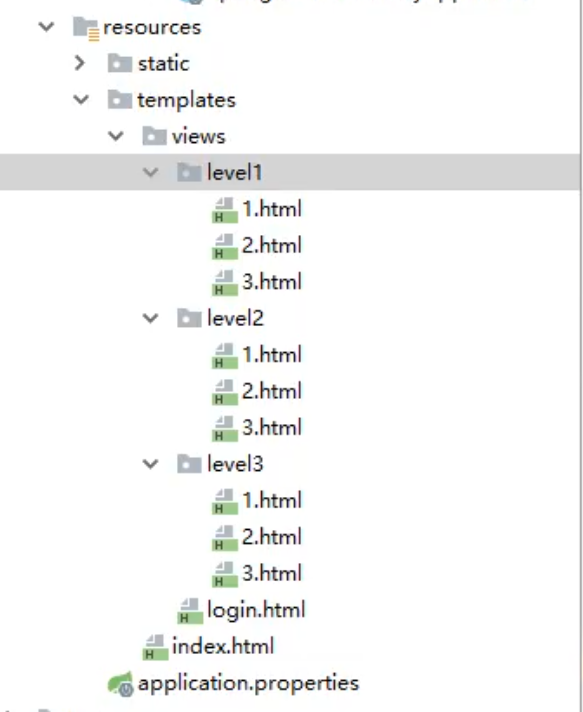
- 编写controller
@Controllerpublic class RouterController { @RequestMapping({"/","/index"}) public String index(){ return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/toLogin") public String toLogin(){ return "views/login"; } @RequestMapping("/level1/{id}") public String level1(@PathVariable("id") int id){ return "views/level1/"+id; } @RequestMapping("/level2/{id}") public String level2(@PathVariable("id") int id){ return "views/level2/"+id; } @RequestMapping("/level3/{id}") public String level3(@PathVariable("id") int id){ return "views/level3/"+id; }}
认证和授权
引入 Spring Security 模块
pom.xm
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId></dependency>
编写基础配置类:AOP思想
参考官网:https://spring.io/projects/spring-security
查看我们自己项目中的版本,找到对应的帮助文档:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.3.0.RELEASE/reference/html5
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启WebSecurity模式public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { }}
重写configure方法,定制请求的授权规则
@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { // 定制请求的授权规则 // 首页所有人可以访问 http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/").permitAll() .antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1") .antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2") .antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3");}
测试一下:发现除了首页都进不去了!因为我们目前没有登录的角色,因为请求需要登录的角色拥有对应的权限才可以!
开启登录功能
在configure()方法中加入以下配置,开启自动配置的登录功能!
// 开启自动配置的登录功能// /login 请求来到登录页// /login?error 重定向到这里表示登录失败http.formLogin();
没有权限的时候,会跳转到登录的页面http://localhost:8080/login
定义认证规则
我们可以定义认证规则,重写configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)方法
这里采用的是auth.inMemoryAuthentication()认证,用数据库的话采用auth.jdbcAuthentication()
//定义认证规则@Overrideprotected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { //在内存中定义,也可以在jdbc中去拿.... //正常应该从数据库中拿 auth.inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("kuangshen").password("123456").roles("vip2","vip3") .and() .withUser("root").password("123456").roles("vip1","vip2","vip3") .and() .withUser("guest").password("123456").roles("vip1","vip2");}
使用这些账号登录进行测试!发现会报错!
There is no PasswordEncoder mapped for the id “null”
原因,我们要将前端传过来的密码进行某种方式加密,否则就无法登录,修改代码
//定义认证规则@Overrideprotected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { //在内存中定义,也可以在jdbc中去拿.... //Spring security 5.0中新增了多种加密方式,也改变了密码的格式。 //要想我们的项目还能够正常登陆,需要修改一下configure中的代码。我们要将前端传过来的密码进行某种方式加密 //spring security 官方推荐的是使用bcrypt加密方式。 auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder()) .withUser("kuangshen").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip2","vip3") .and() .withUser("root").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2","vip3") .and() .withUser("guest").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2");}
权限控制和注销
1、开启自动配置的注销的功能
//定制请求的授权规则@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { //.... //开启自动配置的注销的功能 // /logout 注销请求 http.logout();}
2、我们在前端,增加一个注销的按钮,index.html 导航栏中
<a class="item" th:href="@{/logout}"> <i class="address card icon"></i> 注销</a>
3、我们可以去测试一下,登录成功后点击注销,发现注销完毕会跳转到登录页面!
4、但是,我们想让他注销成功后,依旧可以跳转到首页,该怎么处理呢?
// .logoutSuccessUrl("/"); 注销成功来到首页http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/");
5、测试,注销完毕后,发现跳转到首页OK
6、我们现在又来一个需求:用户没有登录的时候,导航栏上只显示登录按钮,用户登录之后,导航栏可以显示登录的用户信息及注销按钮!还有就是,比如kuangshen这个用户,它只有 vip2,vip3功能,那么登录则只显示这两个功能,而vip1的功能菜单不显示!这个就是真实的网站情况了!该如何做呢?
我们需要结合thymeleaf中的一些功能
sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()":是否认证登录!来显示不同的页面
Maven依赖:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.thymeleaf.extras/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity4 --><dependency> <groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5</artifactId> <version>3.0.4.RELEASE</version></dependency>
7、修改我们的 前端页面
-
导入命名空间
-
xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5" -
修改导航栏,增加认证判断
-
<!--登录注销--><div class="right menu"> <!--如果未登录--> <div sec:authorize="!isAuthenticated()"> <a class="item" th:href="@{/login}"> <i class="address card icon"></i> 登录 </a> </div> <!--如果已登录--> <div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()"> <a class="item"> <i class="address card icon"></i> 用户名:<span sec:authentication="principal.username"></span> 角色:<span sec:authentication="principal.authorities"></span> </a> </div> <div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()"> <a class="item" th:href="@{/logout}"> <i class="address card icon"></i> 注销 </a> </div></div>
8、重启测试,我们可以登录试试看,登录成功后确实,显示了我们想要的页面;
9、如果注销404了,就是因为它默认防止csrf跨站请求伪造,因为会产生安全问题,我们可以将请求改为post表单提交,或者在spring security中关闭csrf功能;我们试试:在 配置中增加 http.csrf().disable();
http.csrf().disable();//关闭csrf功能:跨站请求伪造,默认只能通过post方式提交logout请求http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/");
10、我们继续将下面的角色功能块认证完成!
<!-- sec:authorize="hasRole('vip1')" --><div class="column" sec:authorize="hasRole('vip1')"> <div class="ui raised segment"> <div class="ui"> <div class="content"> <h5 class="content">Level 1</h5> <hr> <div><a th:href="@{/level1/1}"><i class="bullhorn icon"></i> Level-1-1</a></div> <div><a th:href="@{/level1/2}"><i class="bullhorn icon"></i> Level-1-2</a></div> <div><a th:href="@{/level1/3}"><i class="bullhorn icon"></i> Level-1-3</a></div> </div> </div> </div></div><div class="column" sec:authorize="hasRole('vip2')"> <div class="ui raised segment"> <div class="ui"> <div class="content"> <h5 class="content">Level 2</h5> <hr> <div><a th:href="@{/level2/1}"><i class="bullhorn icon"></i> Level-2-1</a></div> <div><a th:href="@{/level2/2}"><i class="bullhorn icon"></i> Level-2-2</a></div> <div><a th:href="@{/level2/3}"><i class="bullhorn icon"></i> Level-2-3</a></div> </div> </div> </div></div><div class="column" sec:authorize="hasRole('vip3')"> <div class="ui raised segment"> <div class="ui"> <div class="content"> <h5 class="content">Level 3</h5> <hr> <div><a th:href="@{/level3/1}"><i class="bullhorn icon"></i> Level-3-1</a></div> <div><a th:href="@{/level3/2}"><i class="bullhorn icon"></i> Level-3-2</a></div> <div><a th:href="@{/level3/3}"><i class="bullhorn icon"></i> Level-3-3</a></div> </div> </div> </div></div>
11、测试一下!
12、权限控制和注销搞定!
记住我
现在的情况,我们只要登录之后,关闭浏览器,再登录,就会让我们重新登录,但是很多网站的情况,就是有一个记住密码的功能,这个该如何实现呢?很简单
1、开启记住我功能
//定制请求的授权规则@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {//。。。。。。。。。。。 //记住我 http.rememberMe();}
2、我们再次启动项目测试一下,发现登录页多了一个记住我功能,我们登录之后关闭 浏览器,然后重新打开浏览器访问,发现用户依旧存在!
思考:如何实现的呢?其实非常简单
我们可以查看浏览器的cookie
3、我们点击注销的时候,可以发现,spring security 帮我们自动删除了这个 cookie
4、结论:登录成功后,将cookie发送给浏览器保存,以后登录带上这个cookie,只要通过检查就可以免登录了。如果点击注销,则会删除这个cookie,具体的原理我们在JavaWeb阶段都讲过了,这里就不在多说了!
定制登录页
现在这个登录页面都是spring security 默认的,怎么样可以使用我们自己写的Login界面呢?
1、在刚才的登录页配置后面指定 loginpage
http.formLogin().loginPage("/toLogin");
2、然后前端也需要指向我们自己定义的 login请求
<a class="item" th:href="@{/toLogin}"> <i class="address card icon"></i> 登录</a>
3、我们登录,需要将这些信息发送到哪里,我们也需要配置,login.html 配置提交请求及方式,方式必须为post:
在 loginPage()源码中的注释上有写明:
<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post"> <div class="field"> <label>Username</label> <div class="ui left icon input"> <input type="text" placeholder="Username" name="username"> <i class="user icon"></i> </div> </div> <div class="field"> <label>Password</label> <div class="ui left icon input"> <input type="password" name="password"> <i class="lock icon"></i> </div> </div> <input type="submit" class="ui blue submit button"/></form>
4、这个请求提交上来,我们还需要验证处理,怎么做呢?我们可以查看formLogin()方法的源码!我们配置接收登录的用户名和密码的参数!
http.formLogin() .usernameParameter("username") .passwordParameter("password") .loginPage("/toLogin") .loginProcessingUrl("/login"); // 登陆表单提交请求
5、在登录页增加记住我的多选框
<input type="checkbox" name="remember"> 记住我
6、后端验证处理!
//定制记住我的参数!http.rememberMe().rememberMeParameter("remember");
7、测试,OK
完整配置代码
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//定制请求的授权规则
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1")
.antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2")
.antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3");
//开启自动配置的登录功能:如果没有权限,就会跳转到登录页面!
// /login 请求来到登录页
// /login?error 重定向到这里表示登录失败
http.formLogin()
.usernameParameter("username")
.passwordParameter("password")
.loginPage("/toLogin")
.loginProcessingUrl("/login"); // 登陆表单提交请求
//开启自动配置的注销的功能
// /logout 注销请求
// .logoutSuccessUrl("/"); 注销成功来到首页
http.csrf().disable();//关闭csrf功能:跨站请求伪造,默认只能通过post方式提交logout请求
http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/");
//记住我
http.rememberMe().rememberMeParameter("remember");
}
//定义认证规则
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//在内存中定义,也可以在jdbc中去拿....
//Spring security 5.0中新增了多种加密方式,也改变了密码的格式。
//要想我们的项目还能够正常登陆,需要修改一下configure中的代码。我们要将前端传过来的密码进行某种方式加密
//spring security 官方推荐的是使用bcrypt加密方式。
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder())
.withUser("kuangshen").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip2","vip3")
.and()
.withUser("root").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2","vip3")
.and()
.withUser("guest").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2");
}
}
13、Swagger
13.1、Swagger简介
前后端分离
- 前端 -> 前端控制层、视图层
- 后端 -> 后端控制层、服务层、数据访问层
- 前后端通过API进行交互
- 前后端相对独立且松耦合
产生的问题
- 前后端集成,前端或者后端无法做到“及时协商,尽早解决”,最终导致问题集中爆发
解决方案
- 首先定义schema [ 计划的提纲 ],并实时跟踪最新的API,降低集成风险
Swagger
- 号称世界上最流行的API框架
- Restful Api 文档在线自动生成器 => API 文档 与API 定义同步更新
- 直接运行,在线测试API
- 支持多种语言 (如:Java,PHP等)
- 官网:https://swagger.io/
13.2、SpringBoot集成Swagger
SpringBoot集成Swagger => springfox,两个jar包
- Springfox-swagger2
- swagger-springmvc
使用Swagger
要求:jdk 1.8 + 否则swagger2无法运行
集成Swagger
1、新建一个SpringBoot-web项目
2、添加Maven依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger-ui -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
3、编写一个配置类-SwaggerConfig来配置 Swagger
@Configuration //配置类
@EnableSwagger2// 开启Swagger2的自动配置
public class SwaggerConfig {
}
4、访问测试 :http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html ,可以看到swagger的界面;
配置Swagger
1、Swagger实例Bean是Docket,所以通过配置Docket实例来配置Swaggger。
@Bean //配置docket以配置Swagger具体参数
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2);
}
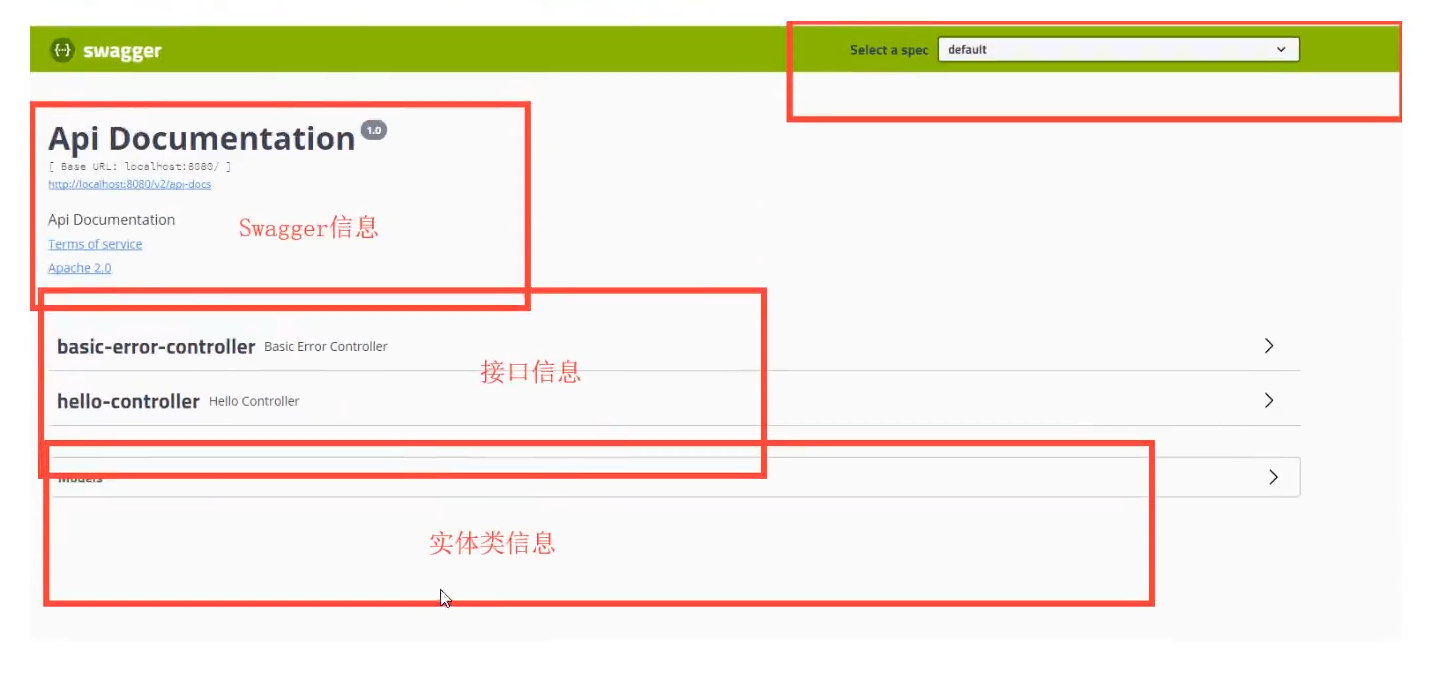
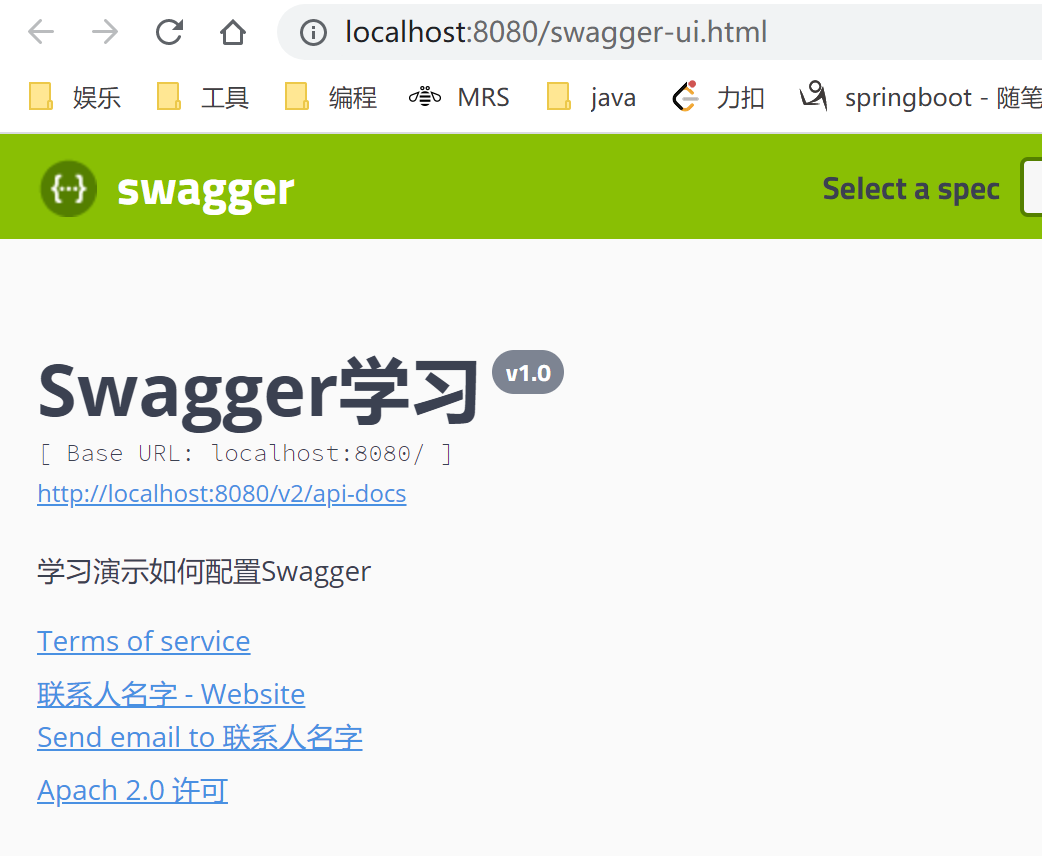
2、可以通过apiInfo()属性配置文档信息
//配置文档信息
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
Contact contact = new Contact("联系人名字", "http://xxx.xxx.com/联系人访问链接", "联系人邮箱");
return new ApiInfo(
"Swagger学习", // 标题
"学习演示如何配置Swagger", // 描述
"v1.0", // 版本
"http://terms.service.url/组织链接", // 组织链接
contact, // 联系人信息
"Apach 2.0 许可", // 许可
"许可链接", // 许可连接
new ArrayList()// 扩展
);
}
3、Docket 实例关联上 apiInfo()
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
4、重启项目,访问测试 http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html 看下效果;
配置扫描接口
1、构建Docket时通过select()方法配置怎么扫描接口。
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()// 通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
.build();
}
2、重启项目测试,由于我们配置根据包的路径扫描接口,所以我们只能看到一个类
3、除了通过包路径配置扫描接口外,还可以通过配置其他方式扫描接口,这里注释一下所有的配置方式:
any() // 扫描所有,项目中的所有接口都会被扫描到
none() // 不扫描接口
// 通过方法上的注解扫描,如withMethodAnnotation(GetMapping.class)只扫描get请求
withMethodAnnotation(final Class<? extends Annotation> annotation)
// 通过类上的注解扫描,如.withClassAnnotation(Controller.class)只扫描有controller注解的类中的接口
withClassAnnotation(final Class<? extends Annotation> annotation)
basePackage(final String basePackage) // 根据包路径扫描接口
4、除此之外,我们还可以配置接口扫描过滤:
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()// 通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/kuang开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/kuang/**"))
.build();
}
5、这里的可选值还有
any() // 任何请求都扫描
none() // 任何请求都不扫描
regex(final String pathRegex) // 通过正则表达式控制
ant(final String antPattern) // 通过ant()控制
配置开关
1、通过enable()方法配置是否启用swagger,如果是false,swagger将不能在浏览器中访问了
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.enable(false) //配置是否启用Swagger,如果是false,在浏览器将无法访问
.select()// 通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/kuang开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/kuang/**"))
.build();
}
2、如何动态配置当项目处于test、dev环境时显示swagger,处于prod时不显示?
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment) {
// 设置要显示swagger的环境
Profiles of = Profiles.of("dev", "test");
// 判断当前是否处于该环境
// 通过 enable() 接收此参数判断是否要显示
boolean b = environment.acceptsProfiles(of);
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.enable(b) //配置是否启用Swagger,如果是false,在浏览器将无法访问
.select()// 通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/kuang开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/kuang/**"))
.build();
}
3、可以在项目中增加一个dev的配置文件查看效果!
配置API分组
1、如果没有配置分组,默认是default。通过groupName()方法即可配置分组:
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment) {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo())
.groupName("hello") // 配置分组
// 省略配置....
}
2、重启项目查看分组
3、如何配置多个分组?配置多个分组只需要配置多个docket即可:
@Bean
public Docket docket1(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group1");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket2(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group2");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket3(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group3");
}
4、重启项目查看即可
实体配置
1、新建一个实体类
@ApiModel("用户实体")
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
public String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
public String password;
}
2、只要这个实体在请求接口的返回值上(即使是泛型),都能映射到实体项中:
@RequestMapping("/getUser")
public User getUser(){
return new User();
}
3、重启查看测试
注:并不是因为@ApiModel这个注解让实体显示在这里了,而是只要出现在接口方法的返回值上的实体都会显示在这里,而@ApiModel和@ApiModelProperty这两个注解只是为实体添加注释的。
@ApiModel为类添加注释
@ApiModelProperty为类属性添加注释
常用注解
Swagger的所有注解定义在io.swagger.annotations包下
下面列一些经常用到的,未列举出来的可以另行查阅说明:
| Swagger注解 | 简单说明 |
|---|---|
| @Api(tags = "xxx模块说明") | 作用在模块类上 |
| @ApiOperation("xxx接口说明") | 作用在接口方法上 |
| @ApiModel("xxxPOJO说明") | 作用在模型类上:如VO、BO |
| @ApiModelProperty(value = "xxx属性说明",hidden = true) | 作用在类方法和属性上,hidden设置为true可以隐藏该属性 |
| @ApiParam("xxx参数说明") | 作用在参数、方法和字段上,类似@ApiModelProperty |
我们也可以给请求的接口配置一些注释
@ApiOperation("狂神的接口")
@PostMapping("/kuang")
@ResponseBody
public String kuang(@ApiParam("这个名字会被返回")String username){
return username;
}
这样的话,可以给一些比较难理解的属性或者接口,增加一些配置信息,让人更容易阅读!
相较于传统的Postman或Curl方式测试接口,使用swagger简直就是傻瓜式操作,不需要额外说明文档(写得好本身就是文档)而且更不容易出错,只需要录入数据然后点击Execute,如果再配合自动化框架,可以说基本就不需要人为操作了。
Swagger是个优秀的工具,现在国内已经有很多的中小型互联网公司都在使用它,相较于传统的要先出Word接口文档再测试的方式,显然这样也更符合现在的快速迭代开发行情。当然了,提醒下大家在正式环境要记得关闭Swagger,一来出于安全考虑二来也可以节省运行时内存。
拓展:其他皮肤
我们可以导入不同的包实现不同的皮肤定义:
1、默认的 访问 http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
2、bootstrap-ui 访问 http://localhost:8080/doc.html
<!-- 引入swagger-bootstrap-ui包 /doc.html-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.xiaoymin</groupId>
<artifactId>swagger-bootstrap-ui</artifactId>
<version>1.9.1</version>
</dependency>
3、Layui-ui 访问 http://localhost:8080/docs.html
<!-- 引入swagger-ui-layer包 /docs.html-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.caspar-chen</groupId>
<artifactId>swagger-ui-layer</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
</dependency>
4、mg-ui 访问 http://localhost:8080/document.html
<!-- 引入swagger-ui-layer包 /document.html-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.zyplayer</groupId>
<artifactId>swagger-mg-ui</artifactId>
<version>1.0.6</version>
</dependency>
14、任务
在我们的工作中,常常会用到异步处理任务,比如我们在网站上发送邮件,后台会去发送邮件,此时前台会造成响应不动,直到邮件发送完毕,响应才会成功,所以我们一般会采用多线程的方式去处理这些任务。还有一些定时任务,比如需要在每天凌晨的时候,分析一次前一天的日志信息。还有就是邮件的发送,微信的前身也是邮件服务呢?这些东西都是怎么实现的呢?其实SpringBoot都给我们提供了对应的支持,我们上手使用十分的简单,只需要开启一些注解支持,配置一些配置文件即可!
14.1、异步任务
1、创建一个service包
2、创建一个类AsyncService
异步处理还是非常常用的,比如我们在网站上发送邮件,后台会去发送邮件,此时前台会造成响应不动,直到邮件发送完毕,响应才会成功,所以我们一般会采用多线程的方式去处理这些任务。
编写方法,假装正在处理数据,使用线程设置一些延时,模拟同步等待的情况;
@Service
public class AsyncService {
public void hello(){
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("业务进行中....");
}
}
3、编写controller包
4、编写AsyncController类
我们去写一个Controller测试一下
@RestController
public class AsyncController {
@Autowired
AsyncService asyncService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
asyncService.hello();
return "success";
}
}
5、访问http://localhost:8080/hello进行测试,3秒后出现success,这是同步等待的情况。
问题:我们如果想让用户直接得到消息,就在后台使用多线程的方式进行处理即可,但是每次都需要自己手动去编写多线程的实现的话,太麻烦了,我们只需要用一个简单的办法,在我们的方法上加一个简单的注解即可,如下:
6、给hello方法添加**@Async注解**;
//告诉Spring这是一个异步方法
@Async
public void hello(){
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("业务进行中....");
}
7、SpringBoot就会自己开一个线程池,进行调用!但是要让这个注解生效,我们还需要在主程序上添加一个注解**@EnableAsync ,开启异步注解功能**;
@EnableAsync //开启异步注解功能
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootTaskApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootTaskApplication.class, args);
}
}
7、重启测试,网页瞬间响应,后台代码依旧执行!
14.2、邮件任务
邮件发送,在我们的日常开发中,也非常的多,Springboot也帮我们做了支持
- 邮件发送需要引入spring-boot-start-mail
- SpringBoot 自动配置MailSenderAutoConfiguration
- 定义MailProperties内容,配置在application.yml中
- 自动装配JavaMailSender
- 测试邮件发送
测试:
1、引入pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId>
</dependency>
看它引入的依赖,可以看到 jakarta.mail
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.mail</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.mail</artifactId>
<version>1.6.4</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
2、查看自动配置类:MailSenderAutoConfiguration
这个类中存在bean,JavaMailSenderImpl
然后我们去看下配置文件
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.mail"
)
public class MailProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET;
private String host;
private Integer port;
private String username;
private String password;
private String protocol = "smtp";
private Charset defaultEncoding;
private Map<String, String> properties;
private String jndiName;
}
3、配置文件:
spring.mail.username=24736743@qq.com
spring.mail.password=你的qq授权码
spring.mail.host=smtp.qq.com
# qq需要配置ssl 加密验证
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.ssl.enable=true
获取授权码:在QQ邮箱中的设置->账户->开启pop3和smtp服务
4、Spring单元测试
@Autowired
JavaMailSenderImpl mailSender;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
//邮件设置1:一个简单的邮件
SimpleMailMessage message = new SimpleMailMessage();
message.setSubject("通知-明天来狂神这听课");
message.setText("今晚7:30开会");
message.setTo("24736743@qq.com");
message.setFrom("24736743@qq.com");
mailSender.send(message);
}
@Test
public void contextLoads2() throws MessagingException {
//邮件设置2:一个复杂的邮件
MimeMessage mimeMessage = mailSender.createMimeMessage();
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage, true);
helper.setSubject("通知-明天来狂神这听课");
helper.setText("<b style='color:red'>今天 7:30来开会</b>",true);
//发送附件
helper.addAttachment("1.jpg",new File(""));
helper.addAttachment("2.jpg",new File(""));
helper.setTo("24736743@qq.com");
helper.setFrom("24736743@qq.com");
mailSender.send(mimeMessage);
}
查看邮箱,邮件接收成功!
我们只需要使用Thymeleaf进行前后端结合即可开发自己网站邮件收发功能了!
14.3、定时任务
接口
项目开发中经常需要执行一些定时任务,比如需要在每天凌晨的时候,分析一次前一天的日志信息,Spring为我们提供了异步执行任务调度的方式,提供了两个接口。
- TaskExecutor接口:任务执行
- TaskScheduler接口:任务调度
配置
两个注解:
- @EnableScheduling:开启定时功能注解
- @Scheduled:什么时候执行
计划任务cron表达式:
测试步骤:
1、创建一个ScheduledService
我们里面存在一个hello方法,他需要定时执行,怎么处理呢?
@Service
public class ScheduledService {
//秒 分 时 日 月 周几
//0 * * * * MON-FRI
//注意cron表达式的用法;
@Scheduled(cron = "0 * * * * 0-7")
public void hello(){
System.out.println("hello.....");
}
}
2、这里写完定时任务之后,我们需要在主程序上增加@EnableScheduling 开启定时任务功能
@EnableAsync //开启异步注解功能
@EnableScheduling //开启基于注解的定时任务
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootTaskApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootTaskApplication.class, args);
}
}
3、我们来详细了解下cron表达式;
http://www.bejson.com/othertools/cron/
4、常用的表达式
(1)0/2 * * * * ? 表示每2秒 执行任务
(1)0 0/2 * * * ? 表示每2分钟 执行任务
(1)0 0 2 1 * ? 表示在每月的1日的凌晨2点调整任务
(2)0 15 10 ? * MON-FRI 表示周一到周五每天上午10:15执行作业
(3)0 15 10 ? 6L 2002-2006 表示2002-2006年的每个月的最后一个星期五上午10:15执行作
(4)0 0 10,14,16 * * ? 每天上午10点,下午2点,4点
(5)0 0/30 9-17 * * ? 朝九晚五工作时间内每半小时
(6)0 0 12 ? * WED 表示每个星期三中午12点
(7)0 0 12 * * ? 每天中午12点触发
(8)0 15 10 ? * * 每天上午10:15触发
(9)0 15 10 * * ? 每天上午10:15触发
(10)0 15 10 * * ? 每天上午10:15触发
(11)0 15 10 * * ? 2005 2005年的每天上午10:15触发
(12)0 * 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:59期间的每1分钟触发
(13)0 0/5 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:55期间的每5分钟触发
(14)0 0/5 14,18 * * ? 在每天下午2点到2:55期间和下午6点到6:55期间的每5分钟触发
(15)0 0-5 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:05期间的每1分钟触发
(16)0 10,44 14 ? 3 WED 每年三月的星期三的下午2:10和2:44触发
(17)0 15 10 ? * MON-FRI 周一至周五的上午10:15触发
(18)0 15 10 15 * ? 每月15日上午10:15触发
(19)0 15 10 L * ? 每月最后一日的上午10:15触发
(20)0 15 10 ? * 6L 每月的最后一个星期五上午10:15触发
(21)0 15 10 ? * 6L 2002-2005 2002年至2005年的每月的最后一个星期五上午10:15触发
(22)0 15 10 ? * 6#3 每月的第三个星期五上午10:15触发
14、Dubbo和Zookeeper集成
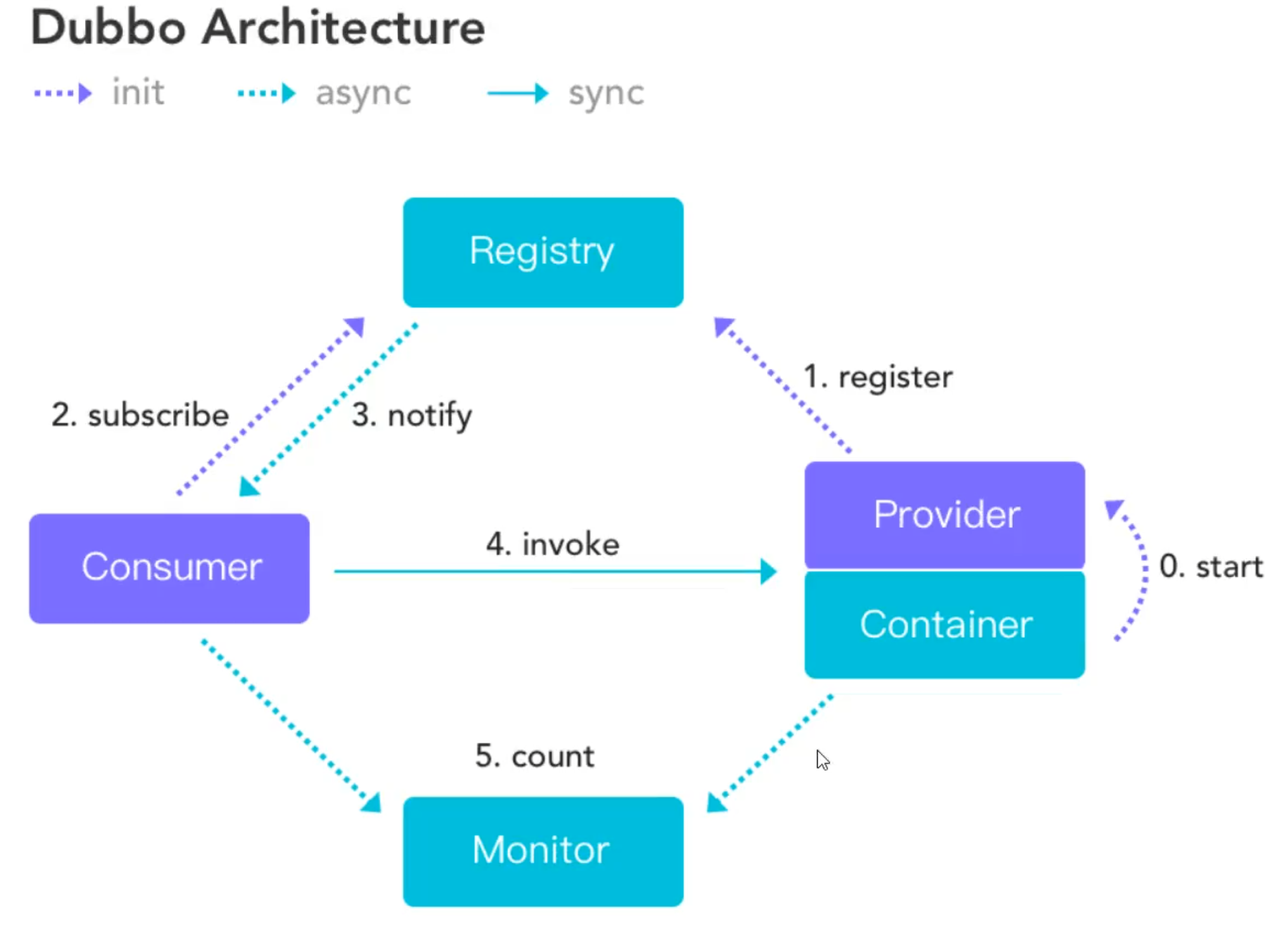
14.1、什么是分布式系统?
在《分布式系统原理与范型》一书中有如下定义:“分布式系统是若干独立计算机的集合,这些计算机对于用户来说就像单个相关系统”;
分布式系统是由一组通过网络进行通信、为了完成共同的任务而协调工作的计算机节点组成的系统。分布式系统的出现是为了用廉价的、普通的机器完成单个计算机无法完成的计算、存储任务。其目的是利用更多的机器,处理更多的数据。
分布式系统(distributed system)是建立在网络之上的软件系统。
首先需要明确的是,只有当单个节点的处理能力无法满足日益增长的计算、存储任务的时候,且硬件的提升(加内存、加磁盘、使用更好的CPU)高昂到得不偿失的时候,应用程序也不能进一步优化的时候,我们才需要考虑分布式系统。因为,分布式系统要解决的问题本身就是和单机系统一样的,而由于分布式系统多节点、通过网络通信的拓扑结构,会引入很多单机系统没有的问题,为了解决这些问题又会引入更多的机制、协议,带来更多的问题
Dubbo文档
随着互联网的发展,网站应用的规模不断扩大,常规的垂直应用架构已无法应对,分布式服务架构以及流动计算架构势在必行,急需一个治理系统确保架构有条不紊的演进。
在Dubbo的官网文档有这样一张图
单一应用架构
当网站流量很小时,只需一个应用,将所有功能都部署在一起,以减少部署节点和成本。此时,用于简化增删改查工作量的数据访问框架(ORM)是关键。
适用于小型网站,小型管理系统,将所有功能都部署到一个功能里,简单易用。
缺点:
1、性能扩展比较难
2、协同开发问题
3、不利于升级维护
垂直应用架构
当访问量逐渐增大,单一应用增加机器带来的加速度越来越小,将应用拆成互不相干的几个应用,以提升效率。此时,用于加速前端页面开发的**Web框架(MVC)**是关键。
通过切分业务来实现各个模块独立部署,降低了维护和部署的难度,团队各司其职更易管理,性能扩展也更方便,更有针对性。
缺点:公用模块无法重复利用,开发性的浪费
分布式服务架构
当垂直应用越来越多,应用之间交互不可避免,将核心业务抽取出来,作为独立的服务,逐渐形成稳定的服务中心,使前端应用能更快速的响应多变的市场需求。此时,用于提高业务复用及整合的**分布式服务框架(RPC)**是关键。
流动计算架构
当服务越来越多,容量的评估,小服务资源的浪费等问题逐渐显现,此时需增加一个调度中心基于访问压力实时管理集群容量,提高集群利用率。此时,用于提高机器利用率的资源调度和治理中心(SOA)[ Service Oriented Architecture]是关键。
14.2、RPC
RPC【Remote Procedure Call】是指远程过程调用,是一种进程间通信方式,他是一种技术的思想,而不是规范。它允许程序调用另一个地址空间(通常是共享网络的另一台机器上)的过程或函数,而不用程序员显式编码这个远程调用的细节。即程序员无论是调用本地的还是远程的函数,本质上编写的调用代码基本相同。
也就是说两台服务器A,B,一个应用部署在A服务器上,想要调用B服务器上应用提供的函数/方法,由于不在一个内存空间,不能直接调用,需要通过网络来表达调用的语义和传达调用的数据。为什么要用RPC呢?就是无法在一个进程内,甚至一个计算机内通过本地调用的方式完成的需求,比如不同的系统间的通讯,甚至不同的组织间的通讯,由于计算能力需要横向扩展,需要在多台机器组成的集群上部署应用。RPC就是要像调用本地的函数一样去调远程函数;
推荐阅读文章:https://www.jianshu.com/p/2accc2840a1b
RPC基本原理
步骤解析:
核心
RPC两个核心模块:
- 通讯
- 序列化
14.3、Dubbo
概述
Apache Dubbo |ˈdʌbəʊ| 是一款高性能、轻量级的开源Java RPC框架,它提供了三大核心能力:
- 面向接口的远程方法调用
- 智能容错和负载均衡
- 服务自动注册和发现
dubbo官网 http://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/index.html
1.了解Dubbo的特性
2.查看官方文档
dubbo基本概念
服务提供者(Provider):暴露服务的服务提供方,服务提供者在启动时,向注册中心注册自己提供的服务。
服务消费者(Consumer):调用远程服务的服务消费方,服务消费者在启动时,向注册中心订阅自己所需的服务,服务消费者,从提供者地址列表中,基于软负载均衡算法,选一台提供者进行调用,如果调用失败,再选另一台调用。
注册中心(Registry):注册中心返回服务提供者地址列表给消费者,如果有变更,注册中心将基于长连接推送变更数据给消费者
监控中心(Monitor):服务消费者和提供者,在内存中累计调用次数和调用时间,定时每分钟发送一次统计数据到监控中心
调用关系说明
l 服务容器负责启动,加载,运行服务提供者。
l 服务提供者在启动时,向注册中心注册自己提供的服务。
l 服务消费者在启动时,向注册中心订阅自己所需的服务。
l 注册中心返回服务提供者地址列表给消费者,如果有变更,注册中心将基于长连接推送变更数据给消费者。
l 服务消费者,从提供者地址列表中,基于软负载均衡算法,选一台提供者进行调用,如果调用失败,再选另一台调用。
l 服务消费者和提供者,在内存中累计调用次数和调用时间,定时每分钟发送一次统计数据到监控中心。
Dubbo环境搭建
点进dubbo官方文档,推荐我们使用Zookeeper 注册中心
什么是zookeeper呢?可以查看官方文档
顾名思义 zookeeper 就是动物园管理员,他是用来管 hadoop(大象)、Hive(蜜蜂)、pig(小 猪)的管理员, Apache Hbase 和 Apache Solr 的分布式集群都用到了 zookeeper;Zookeeper: 是一个分布式的、开源的程序协调服务,是 hadoop 项目下的一个子项目。他提供的主要功 能包括:配置管理、名字服务、分布式锁、集群管理。
Window下安装zookeeper
1、下载zookeeper :地址, 我们下载3.4.14 , 最新版!解压zookeeper
2、运行/bin/zkServer.cmd ,初次运行会报错,没有zoo.cfg配置文件;
可能遇到问题:闪退 !
解决方案:编辑zkServer.cmd文件末尾添加pause 。这样运行出错就不会退出,会提示错误信息,方便找到原因。
3、修改zoo.cfg配置文件
将conf文件夹下面的zoo_sample.cfg复制一份改名为zoo.cfg即可。
注意几个重要位置:
dataDir=./ 临时数据存储的目录(可写相对路径)
clientPort=2181 zookeeper的端口号
修改完成后再次启动zookeeper
4、使用zkCli.cmd测试
ls /:列出zookeeper根下保存的所有节点
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 4] ls /
[zookeeper]
create –e /kuangshen 123:创建一个kuangshen节点,值为123
get /kuangshen:获取/kuangshen节点的值
我们再来查看一下节点
window下安装dubbo-admin
dubbo本身并不是一个服务软件。它其实就是一个jar包,能够帮你的java程序连接到zookeeper,并利用zookeeper消费、提供服务。
但是为了让用户更好的管理监控众多的dubbo服务,官方提供了一个可视化的监控程序dubbo-admin,不过这个监控即使不装也不影响使用。
我们这里来安装一下:
1、下载dubbo-admin
地址 :https://github.com/apache/dubbo-admin/tree/master
2、解压进入目录
修改 dubbo-admin\src\main\resources \application.properties 指定zookeeper地址
server.port=7001
spring.velocity.cache=false
spring.velocity.charset=UTF-8
spring.velocity.layout-url=/templates/default.vm
spring.messages.fallback-to-system-locale=false
spring.messages.basename=i18n/message
spring.root.password=root
spring.guest.password=guest
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
3、在项目目录下打包dubbo-admin
mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true
第一次打包的过程有点慢,需要耐心等待!直到成功!
4、执行 dubbo-admin\target 下的dubbo-admin-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
java -jar dubbo-admin-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
【注意:zookeeper的服务一定要打开!】
执行完毕,我们去访问一下 http://localhost:7001/ , 这时候我们需要输入登录账户和密码,我们都是默认的root-root;
登录成功后,查看界面
安装完成!
14.4、SpringBoot + Dubbo + zookeeper
框架搭建
1. 启动zookeeper !
2. IDEA创建一个空项目;
3.创建一个模块,实现服务提供者:provider-server , 选择web依赖即可
4.项目创建完毕,我们写一个服务,比如卖票的服务;
编写接口
package com.kuang.provider.service;
public interface TicketService {
public String getTicket();
}
编写实现类
package com.kuang.provider.service;
public class TicketServiceImpl implements TicketService {
@Override
public String getTicket() {
return "《狂神说Java》";
}
}
5.创建一个模块,实现服务消费者:consumer-server , 选择web依赖即可
6.项目创建完毕,我们写一个服务,比如用户的服务;
编写service
package com.kuang.consumer.service;
public class UserService {
//我们需要去拿去注册中心的服务
}
需求:现在我们的用户想使用买票的服务,这要怎么弄呢 ?
服务提供者
1、将服务提供者注册到注册中心,我们需要整合Dubbo和zookeeper,所以需要导包
我们从dubbo官网进入github,看下方的帮助文档,找到dubbo-springboot,找到依赖包
<!-- Dubbo Spring Boot Starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.7.3</version>
</dependency>
zookeeper的包我们去maven仓库下载,zkclient;
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.github.sgroschupf/zkclient -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.sgroschupf</groupId>
<artifactId>zkclient</artifactId>
<version>0.1</version>
</dependency>
【新版的坑】zookeeper及其依赖包,解决日志冲突,还需要剔除日志依赖;
<!-- 引入zookeeper -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId>
<version>2.12.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId>
<version>2.12.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeeper</groupId>
<artifactId>zookeeper</artifactId>
<version>3.4.14</version>
<!--排除这个slf4j-log4j12-->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
2、在springboot配置文件中配置dubbo相关属性!
#当前应用名字
dubbo.application.name=provider-server
#注册中心地址
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
#扫描指定包下服务
dubbo.scan.base-packages=com.kuang.provider.service
3、在service的实现类中配置服务注解,发布服务!注意导包问题
import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.Service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Service //将服务发布出去
@Component //放在容器中
public class TicketServiceImpl implements TicketService {
@Override
public String getTicket() {
return "《狂神说Java》";
}
}
逻辑理解 :应用启动起来,dubbo就会扫描指定的包下带有@component注解的服务,将它发布在指定的注册中心中!
服务消费者
1、导入依赖,和之前的依赖一样;
<!--dubbo-->
<!-- Dubbo Spring Boot Starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.7.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--zookeeper-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.github.sgroschupf/zkclient -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.sgroschupf</groupId>
<artifactId>zkclient</artifactId>
<version>0.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入zookeeper -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId>
<version>2.12.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId>
<version>2.12.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeeper</groupId>
<artifactId>zookeeper</artifactId>
<version>3.4.14</version>
<!--排除这个slf4j-log4j12-->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
2、配置参数
#当前应用名字
dubbo.application.name=consumer-server
#注册中心地址
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
3. 本来正常步骤是需要将服务提供者的接口打包,然后用pom文件导入,我们这里使用简单的方式,直接将服务的接口拿过来,路径必须保证正确,即和服务提供者相同;
4. 完善消费者的服务类
import com.kuang.provider.service.TicketService;
import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.Reference;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service //注入到容器中
public class UserService {
@Reference //远程引用指定的服务,他会按照全类名进行匹配,看谁给注册中心注册了这个全类名
TicketService ticketService;
public void bugTicket(){
String ticket = ticketService.getTicket();
System.out.println("在注册中心买到"+ticket);
}
}
5. 测试类编写;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class ConsumerServerApplicationTests {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
userService.bugTicket();
}
}
启动测试
1. 开启zookeeper
2. 打开dubbo-admin实现监控【可以不用做】
3. 开启服务者
4. 消费者消费测试,结果:
监控中心 :
ok , 这就是SpingBoot + dubbo + zookeeper实现分布式开发的应用,其实就是一个服务拆分的思想;